题目
INFO20003_2025_SM2 MINI Practice Exam
匹配题
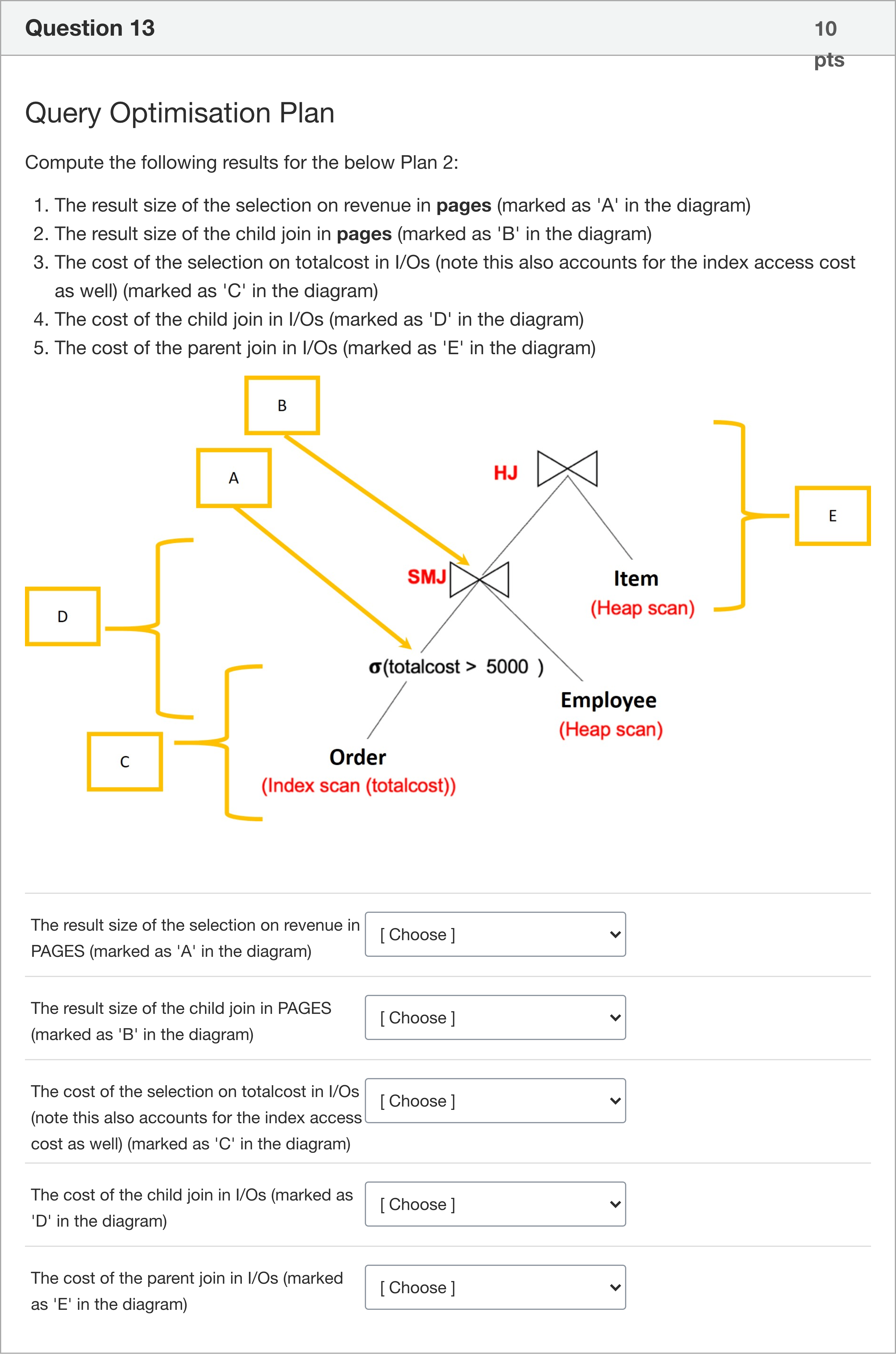
Query Optimisation Plan Compute the following results for the below Plan 2: The result size of the selection on revenue in pages (marked as 'A' in the diagram) The result size of the child join in pages (marked as 'B' in the diagram) The cost of the selection on totalcost in I/Os (note this also accounts for the index access cost as well) (marked as 'C' in the diagram) The cost of the child join in I/Os (marked as 'D' in the diagram) The cost of the parent join in I/Os (marked as 'E' in the diagram) 1: The result size of the selection on revenue in PAGES (marked as 'A' in the diagram) 2: The result size of the child join in PAGES (marked as 'B' in the diagram) 3: The cost of the selection on totalcost in I/Os (note this also accounts for the index access cost as well) (marked as 'C' in the diagram) 4: The cost of the child join in I/Os (marked as 'D' in the diagram) 5: The cost of the parent join in I/Os (marked as 'E' in the diagram)
选项
A.6,000
B.9,040
C.9,200
D.3,000
E.24,050
F.18,040
G.6,300
H.300,000
I.3,025
J.6,050
K.12,050
查看解析
标准答案
Please login to view
思路分析
We start by restating the task and the given data so the reasoning is grounded in the exact items to be matched.
- Question asks to compute five results for Plan 2: A, B, C, D, E.
- The user-provided answer set (to be evaluated) is: 1) 3,000 2) 3,000 3) 3,025 4) 12,050 5) 6,300.
- The answer options available for matching are: 6,000; 9,040; 9,200; 3,000; 24,050; 18,040; 6,300; 300,000; 3,025; 6,050; 12,050.
Now, evaluate each item in sequence, explaining why the chosen option fits or not. I’ll consider what each item represents in the plan and how the numbers typically arise in a query optimization context.
1) The result size of the selection on revenue in PAGES (marked as 'A')
- The candidate choice given is 3,000.
- Reasoning: The result size of a selection on revenue depends on the selectivity of the revenue predicate and any filtering early in the plan. If the diagram/plan indicates a modest filter that reduces the input to about 3,000 pages, then 3,000 is a plausible result size for A. Alternatives like 6,000 or 9,040 would imply a larger than expected reduction or an accumulation from multiple input sources, which might not align with the depicted single-selectivity step. Very large numbers such as 300,000 would indicate an almost full-table outcome, which is unlikely for a selective reven......Login to view full explanation登录即可查看完整答案
我们收录了全球超50000道考试原题与详细解析,现在登录,立即获得答案。
类似问题
Query Optimisation Plan 2 Compute the following results for the below Plan 2: The result size of the selection on vendor in pages (marked as 'A' in the diagram) The result size of the child join in pages (marked as 'B' in the diagram) The cost of the selection on vendor in I/Os (note this also accounts for the index access cost as well) (marked as 'C' in the diagram) The cost of the child join in I/Os (marked as 'D' in the diagram) The cost of the parent join in I/Os (marked as 'E' in the diagram) Figure 3.3.2: PLAN 2. 1: The result size of the selection on Vendor in PAGES (marked as 'A' in the diagram) 2: The result size of the child join in PAGES (marked as 'B' in the diagram) 3: The cost of the selection on Vendor in I/Os (note this also accounts for the index access cost as well) (marked as 'C' in the diagram) 4: The cost of the child join in I/Os (marked as 'D' in the diagram) 5: The cost of the parent join in I/Os (marked as 'E' in the diagram)
Query Optimisation Plan 1 Compute the following results for the below Plan 1: The result size of the child join in pages (marked as 'A' in the diagram) The cost of the child join in I/Os (marked as 'B' in the diagram). The cost of the parent join in I/Os (marked as 'C' in the diagram) Figure 3.3.1: PLAN 1. 1: The result size of the child join in PAGES (marked as 'A' in the diagram) 2: The cost of the child join in I/Os (marked as 'B' in the diagram) 3: The cost of the parent join in I/Os (marked as 'C' in the diagram)
Single Relation Plan C What would happen if our query changed and became: SELECT hotspotID FROM hotspot WHERE postcode = 2600 AND establishmentYear > 2020 AND establishmentYear < 2022; Assuming that the unclustered B+tree index on establishmentYear from the previous question is the only index available, would the cost of the best plan change?
Single Relation Plan B Compute the estimated cost of plan alternatives, assuming that an unclustered B+tree index on (establishmentYear) is the only index available. Suppose there are 10 index pages. Give the lowest (estimated) cost in I/Os after considering all access methods available. Round up any decimals to the nearest integer (e.g., 3.3 rounds up to 4).
更多留学生实用工具
希望你的学习变得更简单
加入我们,立即解锁 海量真题 与 独家解析,让复习快人一步!