你还在为考试焦头烂额?找我们就对了!
我们知道现在是考试月,你正在为了考试复习到焦头烂额。为了让更多留学生在备考与学习季更轻松,我们决定将Gold会员限时免费开放至2025年12月31日!原价£29.99每月,如今登录即享!无门槛领取。
助你高效冲刺备考!
题目
BU.520.601.T2.FA25 Final Exam
判断题
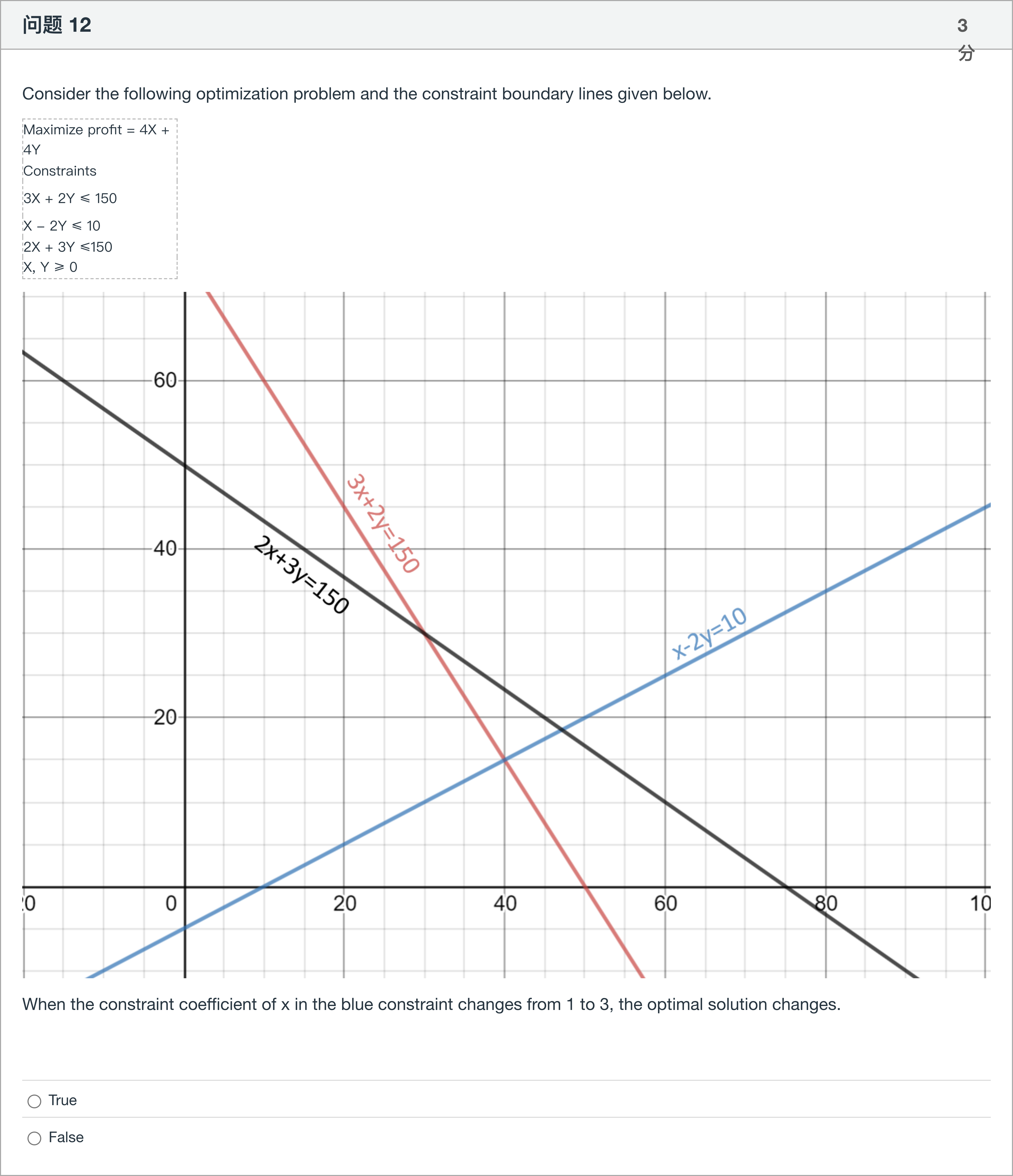
Consider the following optimization problem and the constraint boundary lines given below. Maximize profit = 4X + 4Y Constraints 3X + 2Y ≤ 150 X - 2Y ≤ 10 2X + 3Y ≤150 X, Y ≥ 0 When the constraint coefficient of x in the blue constraint changes from 1 to 3, the optimal solution changes.
选项
A.True
B.False
查看解析
标准答案
Please login to view
思路分析
To analyze whether altering the blue constraint from 1x - 2y ≤ 10 to 3x - 2y ≤ 10 can change the optimal solution, we first restate the problem and the options in our own words. The goal is to maximize profit 4X + 4Y, which is equivalent to maximizing X + Y, subject to the three constraints 3X + 2Y ≤ 150, X - 2Y ≤ 10, 2X + 3Y ≤ 150, and X, Y ≥ 0. The blue constraint line originally has the form X - 2Y = 10 (slope 1/2 when solved for Y), and would become 3X - 2Y = 10 (slope 3/2 when solved for Y) if the coefficient of X changes from 1 to 3.
Option 1 (true): The claim is that changing the coefficient of ......Login to view full explanation登录即可查看完整答案
我们收录了全球超50000道考试原题与详细解析,现在登录,立即获得答案。
类似问题
Solving a linear program can never result in integer values for the decision variables.
Consider the following optimization problem and the constraint boundary lines given below. Maximize profit = 4X + 4Y Constraints 3X + 2Y ≤ 150 X - 2Y ≤ 10 2X + 3Y ≤150 X, Y ≥ 0 If we increase the objective function coefficient of x by 2, i.e., 4 becomes 6, the new optimal solution includes point C.
Consider the following Excel sensitivity report and it's accompanying problem: Minimize cost = X + 2Y subject to X + 3Y ≥ 90 8X + 2Y ≥ 160 3X + 2Y ≥120 Y ≤ 70 X, Y≥ 0 Variable Cells Final Reduced Objective Allowable Allowable Cell Name Value Cost Coefficient Increase Decrease $B$3 X 25.71 0 1 2 0.333333333 $C$3 Y 21.43 0 2 1 1.333333333 Constraints Final Shadow Constraint Allowable Allowable Cell Name Value Price R.H. Side Increase Decrease $J$6 LHS 90 0.57 90 62 50 $J$7 LHS 248.57 0 160 88.57142857 1E+30 $J$8 LHS 120 0.14 120 150 28.18181818 $J$9 LHS 21.43 0 70 1E+30 48.57142857 Suppose we add another variable, x3, with an objective function coefficient of 9, and constraint coefficients of 8, 3, and 5 for the first three constraints, respectively. What is the marginal impact of this new variable on the objective function? (In your calculations round all the numbers to 2 decimals.)
A constraint is binding if it left hand side of a constraint is equal to the right hand side after the optimal solution is plugged into the constraint function.
更多留学生实用工具
希望你的学习变得更简单
为了让更多留学生在备考与学习季更轻松,我们决定将Gold 会员限时免费开放至2025年12月31日!