题目
MAT135H5_F25_ALL SECTIONS 2.2 Preparation Check
多重下拉选择题
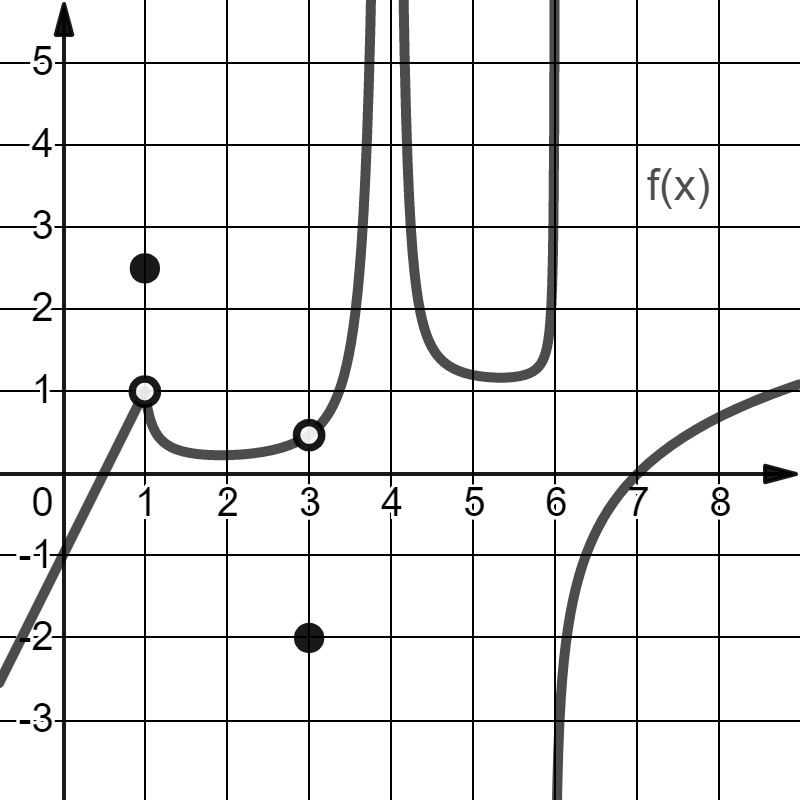
Consider this graph of the function 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) . Which of the following statements are true and which are false? lim 𝑥 → 3 − 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = lim 𝑥 → 3 + 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) [ Select ] False True lim 𝑥 → 1 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = 𝑓 ( 1 ) [ Select ] False True 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) has a vertical asymptote at 𝑥 = 4 . [ Select ] True False 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) has a vertical asymptote at 𝑥 = 6 . [ Select ] False True lim 𝑥 → 4 − 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = lim 𝑥 → 4 + 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) [ Select ] True False lim 𝑥 → 4 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = ∞ [ Select ] False True lim 𝑥 → 6 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = ∞ False The limit lim 𝑥 → 4 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) exists, but lim 𝑥 → 6 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) does not exist. [ Select ] True False
查看解析
标准答案
Please login to view
思路分析
The problem asks you to decide, for each statement, whether it is true or false based on the given graph of f(x). To do this correctly you need to inspect the graph carefully at the specified x-values (3, 1, 4, and 6) and examine one-sided limits, two-sided limits, and the presence of vertical asymptotes or holes. Below is a step-by-step discussion of each statement, with notes where the graph’s exact features are necessary to confirm the conclusion.
1) lim_{x→3^-} f(x) = lim_{x→3^+} f(x)
- What to check: As x approaches 3 from the left and from the right, do the y-values approach the same finite value? If the graph has a removable hole at x = 3 (a point where the function is not defined but the surrounding values approach a common finite y-value), then the two one-sided limits would be equal. If instead the left-hand and right-hand limits approach different numbers, or if either side tends to ±∞, then the equality would be false. Consider any open circles, holes, or jumps near x = 3.
- Why this could be True: If the left and right branches meet at the same finite y-value as x → 3, the two one-sided limits agree.
- Why this could be False: If there is a discontinuity at x = 3 (a hole with a different defined value, a jump, or divergent ......Login to view full explanation登录即可查看完整答案
我们收录了全球超50000道考试原题与详细解析,现在登录,立即获得答案。
类似问题
Suppose that with a certain phone company, an international long distance phone call from Canada to Brazil costs $0.90 for the first minute (up to and including 60 seconds), plus $0.50 for each additional minute or part of a minute. Note: "Part of a minute" means that if a new minute is started even just by one second, a full minute is charged. For example, a 5 min 1 sec phone call costs the same as a 5 min 50 sec phone call and the same as a 6 min 0 sec phone call. Suppose 𝐶 ( 𝑡 ) is the function that gives the cost of making a 𝑡 minute long phone call. On a piece of paper, sketch a graph showing 𝐶 ( 𝑡 ) (with 𝐶 on the 𝑦 -axis and 𝑡 on the 𝑥 -axis). Then use your graph to evaluate each of the following: (Write DNE for undefined.) 𝐶 ( 2.5 ) = [ Select ] DNE 1.9 1.4 2.4 2.9 𝐶 ( 4 ) = [ Select ] 3.4 1.9 2.9 2.4 DNE lim 𝑥 → 3.1 𝐶 ( 𝑡 ) = [ Select ] 1.9 1.4 2.9 2.4 DNE lim 𝑥 → 4 − 𝐶 ( 𝑡 ) = [ Select ] 2.4 1.4 2.9 1.9 DNE lim 𝑥 → 4 + 𝐶 ( 𝑡 ) = [ Select ] DNE 2.9 2.4 3.4 1.9 lim 𝑥 → 4 𝐶 ( 𝑡 ) = [ Select ] 1.9 2.9 DNE 3.4 2.4
Consider this graph of the function 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) . Which of the following statements are true and which are false? lim 𝑥 → 3 − 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = lim 𝑥 → 3 + 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) [ Select ] False True lim 𝑥 → 1 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = 𝑓 ( 1 ) [ Select ] True False 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) has a vertical asymptote at 𝑥 = 4 . [ Select ] False True 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) has a vertical asymptote at 𝑥 = 6 . [ Select ] False True lim 𝑥 → 4 − 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = lim 𝑥 → 4 + 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) [ Select ] False True lim 𝑥 → 4 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = ∞ [ Select ] True False lim 𝑥 → 6 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = ∞ [ Select ] False True The limit lim 𝑥 → 4 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) exists, but lim 𝑥 → 6 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) does not exist. [ Select ] False True
Consider the function 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = { 𝑥 2 + 1 𝑖 𝑓 𝑥 < 2 3 𝑖 𝑓 𝑥 = 2 7 − 𝑥 𝑖 𝑓 𝑥 > 2 . We aim to find out if 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) has a discontinuity at 𝑥 = 2 , and if so, of what type. In order to do that, first find the following information: 𝑓 ( 2 ) = [ Select ] 5 3 2 7 lim 𝑥 ⟶ 2 − 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = [ Select ] 7 3 2 5 lim 𝑥 ⟶ 2 + 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = [ Select ] 5 7 2 3 Is 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) continuous or discontinuous at 𝑥 = 2 ? [ Select ] discontinuous continuous If 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) is discontinuous at 𝑥 = 2 , what type of discontinuity is it? [ Select ] f is continuous An infinite discontinuity A removable discontinuity A jump discontinuity
MTH1010_09_10_3
更多留学生实用工具
希望你的学习变得更简单
加入我们,立即解锁 海量真题 与 独家解析,让复习快人一步!