Still overwhelmed by exam stress? You've come to the right place!
We know exam season has you totally swamped. To support your studies, access Gold Membership for FREE until December 31, 2025! Normally £29.99/month. Just Log In to activate – no strings attached.
Let us help you ace your exams efficiently!
Questions
22108 Accounting and Accountability - Spring 2025 4. PRACTICE Exam - 22108 Spring 2023
Multiple fill-in-the-blank
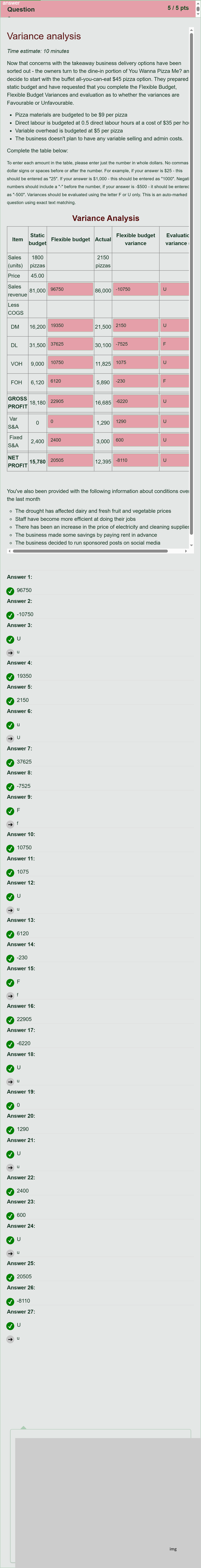
Variance analysis Time estimate: 10 minutes Now that concerns with the takeaway business delivery options have been sorted out - the owners turn to the dine-in portion of You Wanna Pizza Me? and decide to start with the buffet all-you-can-eat $45 pizza option. They prepared a static budget and have requested that you complete the Flexible Budget, Flexible Budget Variances and evaluation as to whether the variances are Favourable or Unfavourable. Pizza materials are budgeted to be $9 per pizza Direct labour is budgeted at 0.5 direct labour hours at a cost of $35 per hour Variable overhead is budgeted at $5 per pizza The business doesn't plan to have any variable selling and admin costs. Complete the table below: To enter each amount in the table, please enter just the number in whole dollars. No commas or dollar signs or spaces before or after the number. For example, if your answer is $25 - this should be entered as "25". If your answer is $1,000 - this should be entered as "1000". Negative numbers should include a "-" before the number, if your answer is -$500 - it should be entered as "-500". Variances should be evaluated using the letter F or U only. This is an auto-marked question using exact text matching. Variance Analysis Item Static budget Flexible budget Actual Flexible budget variance Evaluation of variance (F/U) Sales (units) 1800 pizzas 2150 pizzas Price 45.00 Sales revenue 81,000 [Fill in the blank] 86,000 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] Less COGS DM 16,200 [Fill in the blank] 21,500 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] DL 31,500 [Fill in the blank] 30,100 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] VOH 9,000 [Fill in the blank] 11,825 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] FOH 6,120 [Fill in the blank] 5,890 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] GROSS PROFIT 18,180 [Fill in the blank] 16,685 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] Var S&A 0 [Fill in the blank] 1,290 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] Fixed S&A 2,400 [Fill in the blank] 3,000 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] NET PROFIT 15,780 [Fill in the blank] 12,395 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] You've also been provided with the following information about conditions over the last month The drought has affected dairy and fresh fruit and vegetable prices Staff have become more efficient at doing their jobs There has been an increase in the price of electricity and cleaning supplies The business made some savings by paying rent in advance The business decided to run sponsored posts on social media The manager received a bonus
View Explanation
Standard Answer
Please login to view
Approach Analysis
We start by restating what the task provides and what needs to be filled.
- The scenario: A dine-in buffet with a flexible budget and actual results. Budgeted per pizza: DM $9, DL $35 per hour for 0.5 hour per pizza, VOH $5 per pizza, no variable S&A, and fixed S&A $2,400 (with some changes noted later). Static budget units: 1,800 pizzas. Actual units: 2,150 pizzas.
- Key formulas to use:
- Flexible budget (units = actual quantity): use the per-unit costs given in the budget to compute what costs should be for the actual level of activity.
- Sales revenue (flexible): actual units × budgeted price per unit (here, $45 per pizza).
- Variance = Actual result − Flexible budget amount; evaluate as F (favorable) or U (unfavorable) based on whether Actual is better than Flexible for the business.
- Gross profit (flexible) = Flexible sales revenue − Flexible COGS.
- For fixed overhead, the flexible budget keeps the same amount as the static budget since it does not vary with volume unless stated otherwise.
Proceeding item by item in the order shown and showing the reasoning for each value that appears in the answer field:
1) Sales (units) – Static budget: 1800 pizzas; Flexible budget: 2150 pizzas; Actual: 2150 pizzas
- Flexible sales revenue (based on actual units): 2150 × 45 = 96,750. (This is the value you would enter for the flexible budget revenue in dollars.)
- The provided answer list includes 96,750 as the first numeric entry, which corresponds to the flexible sales revenue for the actual units.
- If y......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
Question at position 3 The following information is available: [table] | Budgeted | Flexed | Actual Output (units) | 600 | 650 | 650 Sales revenue (£) | 420,000 | | 468,000 Raw materials (£) | (24,000) | | (27,300) Labour (£) | (12,000) | | (14,300) Fixed overheads (£) | (126,000) | (126,000) | (110,700) Operating profit (£) | 258,000 | | 315,700 [/table] The variance for operating profit is:£25,700 favourable£64,000 favourable£6300 adverse£70,300 favourableClear my selection
Chris tells you that he budgeted the market size to be around 100,000 frames. However, the actual market size was 130,000 frames. Given this information, calculate the Market Size Variance.
Which of the following interpretations of the materials variances makes sense:
Tell me which statement is consistent with the variances you have calculated so far.
More Practical Tools for International Students
Making Your Study Simpler
To make preparation and study season easier for more international students, we've decided to open up Gold Membership for a limited-time free trial until December 31, 2025!