Questions
SU25-BL-BUS-A325-5063 Exam #3: Summer 2025
Multiple fill-in-the-blank
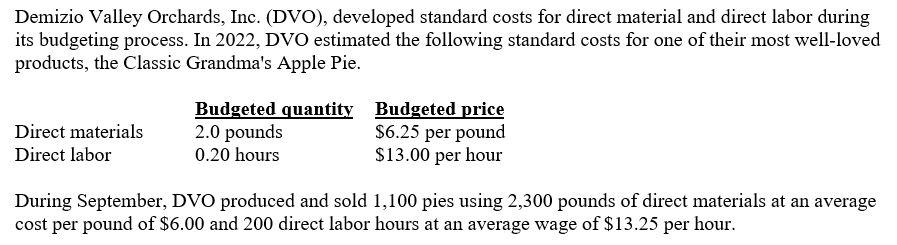
Note: for all answers enter the value as a positive number if it is favorable and a negative number if it is unfavorable. 1. The direct materials price variance is [Fill in the blank], . (9 points) 2. The direct materials efficiency variance is [Fill in the blank], . (9 points) 3. The direct labor price variance is [Fill in the blank], . (9 points) 4. The direct labor efficiency variance is [Fill in the blank], . (9 points)
View Explanation
Verified Answer
Please login to view
Step-by-Step Analysis
Let me restate the given problem and the data used for calculations, then go through each variance one by one with clear steps.
Problem data and setup:
- Budgeted/direct standard costs:
- Direct materials: 2.0 pounds per unit (pie), price $6.25 per pound
- Direct labor: 0.20 hours per unit (pie), wage $13.00 per hour
- Actual for September:
- Pies produced: 1,100
- Direct materials used: 2,300 pounds at an average cost per pound of $6.00
- Direct labor hours: 200 hours at an average wage of $13.25 per hour
- Required variances to fill (all values should be entered as positive if favorable and negative if unfavorable):
1) Direct materials price variance: [Fill in the blank]
2) Direct materials efficiency variance: [Fill in the blank]
3) Direct labor price variance: [Fill in the blank]
4) Direct labor efficiency variance: [Fill in the blank]
Now, analyze each option (or calculation result) step by step:
1) Direct materials price variance
- Use the standard formula: Price variance = (Actual price per unit − Standard price per unit) × Actual quantity purchased.
- Actual price per pound = total di......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
Question at position 3 The following information is available: [table] | Budgeted | Flexed | Actual Output (units) | 600 | 650 | 650 Sales revenue (£) | 420,000 | | 468,000 Raw materials (£) | (24,000) | | (27,300) Labour (£) | (12,000) | | (14,300) Fixed overheads (£) | (126,000) | (126,000) | (110,700) Operating profit (£) | 258,000 | | 315,700 [/table] The variance for operating profit is:£25,700 favourable£64,000 favourable£6300 adverse£70,300 favourableClear my selection
Chris tells you that he budgeted the market size to be around 100,000 frames. However, the actual market size was 130,000 frames. Given this information, calculate the Market Size Variance.
Which of the following interpretations of the materials variances makes sense:
Tell me which statement is consistent with the variances you have calculated so far.
More Practical Tools for Students Powered by AI Study Helper
Making Your Study Simpler
Join us and instantly unlock extensive past papers & exclusive solutions to get a head start on your studies!