你还在为考试焦头烂额?找我们就对了!
我们知道现在是考试月,你正在为了考试复习到焦头烂额。为了让更多留学生在备考与学习季更轻松,我们决定将Gold会员限时免费开放至2025年12月31日!原价£29.99每月,如今登录即享!无门槛领取。
助你高效冲刺备考!
题目
BUSS1040 (ND) Quiz 3: Topics 5-7
简答题
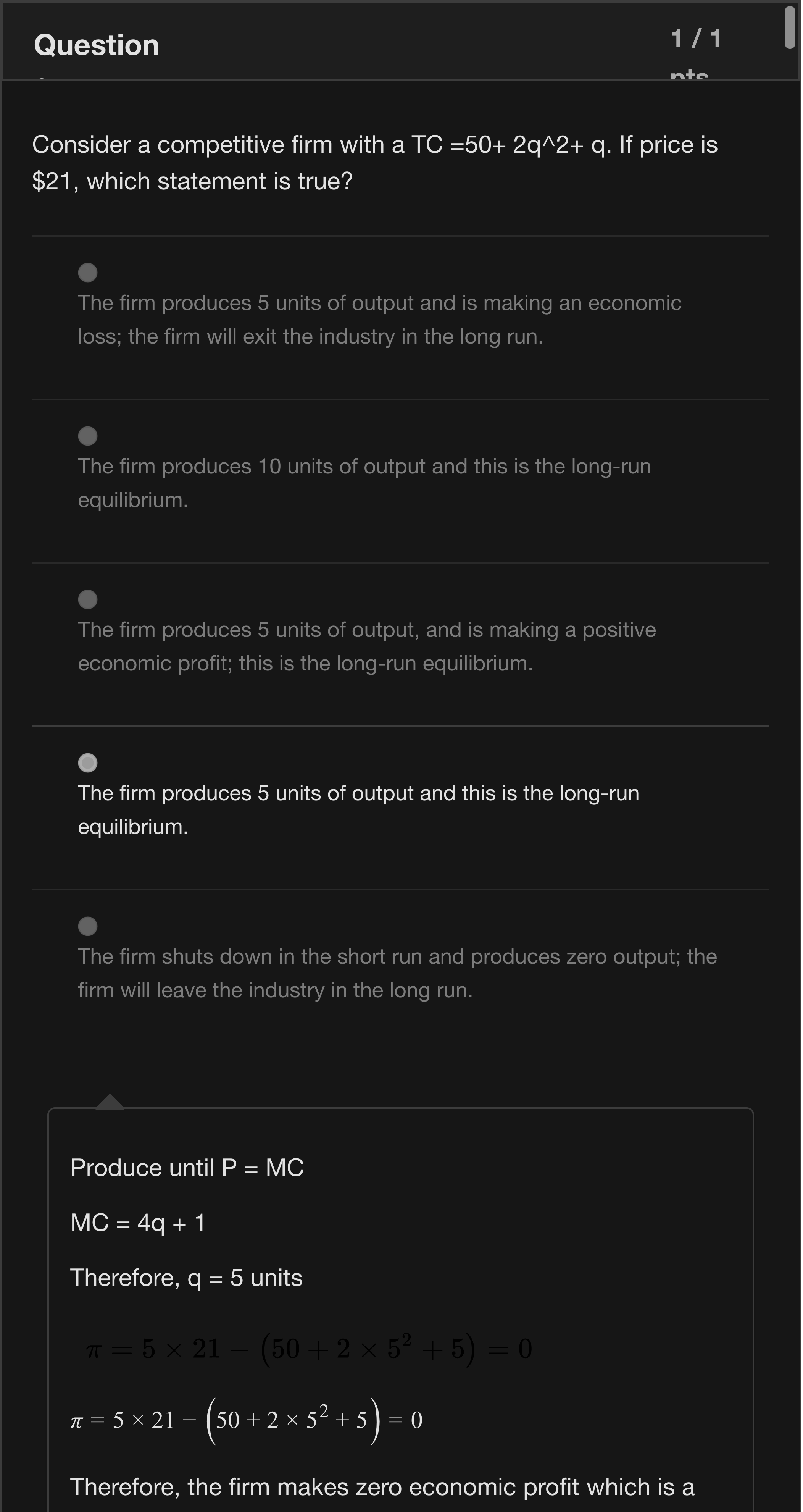
Lihini is a CEO of an opera house called the ‘Lihini’s Opera House”. It is the only opera house in the region, giving Lihini’s Opera House a monopoly position in the market. Each customer’s demand curve for shows per year is given by the following: P = 132 – 6Q. The marginal cost of an extra visitor in a show (i.e., of an extra ticket sold) is $20. Lihini is considering a new pricing scheme for her business: a membership fee that allows people to purchase tickets to the shows after which they can purchase as many opera tickets as they wish for $20 each. If Lihini wants to maximize profits, what is the optimal membership fee that she should charge? [Round your final answer to 2 decimal points when necessary]
查看解析
标准答案
Please login to view
思路分析
We’re evaluating a two-part tariff (membership fee plus per-ticket price) for a monopoly with demand P = 132 − 6Q and constant marginal cost MC = 20 per ticket.
First, set the per-ticket price equal to MC to maximize welfare per unit and allow the fixed membership fee to capture the entire consumer surplus. So ch......Login to view full explanation登录即可查看完整答案
我们收录了全球超50000道考试原题与详细解析,现在登录,立即获得答案。
类似问题
Question at position 8 Section 2: (Hard) Suppose that on weekends 50% of consumers have a demand curve for rides of P = 6 - 0.25Q (“high demand consumers”), and the remaining 50% of consumers have a demand curve for rides of P = 5 – 0.25Q (“low demand consumers”). Because we cannot distinguish these low demand consumers and high demand consumers at the entrance gate, we will be charging the same entry fee (T) and price per unit (P) for both types of consumers. What is the best mix of entry fee (T) and price per ride (P) to maximize profits on weekends?P = MC, T = all CS of high demand customers at that price(none of the choices listed here)P = Monopoly price for low demand customers, T = all CS of of low demand customers at that priceP > MC, T = all CS of high demand customers at that priceP = MC, T = all CS of low demand customers at that priceP > MC, T = all CS of low demand customers at that priceP = Monopoly price for high demand customers, T = all CS of high demand customers at that price
Question at position 6 Section 1: Suppose on weekdays all consumers have a demand curve for rides of P = 6 - 0.25Q. To maximize the profit, you will be choosing the best mix of entry fee (T) and price per ride (P). What would be the price per ride (P)? Provide your answer in numeric form and omit the dollar sign.AnswerSection 1: Suppose on weekdays all consumers have a demand curve for rides of P = 6 - 0.25Q. To maximize the profit, you will be choosing the best mix of entry fee (T) and price per ride (P). What would be the price per ride (P)? Provide your answer in numeric form and omit the dollar sign.[input]
Question at position 4 Two-part tariff refers to a situation in which consumers pay one price (or tariff) for the right to buy as much of a related good as they want at that same price.TrueFalse
For a two-part tariff imposed in a market made up of identical consumers, the fixed fee should be set equal to:
更多留学生实用工具
希望你的学习变得更简单
为了让更多留学生在备考与学习季更轻松,我们决定将Gold 会员限时免费开放至2025年12月31日!