Questions
INFO20003_2025_SM2 Exam: Database Systems (INFO20003_2025_SM2)- Requires Respondus LockDown Browser
Matching
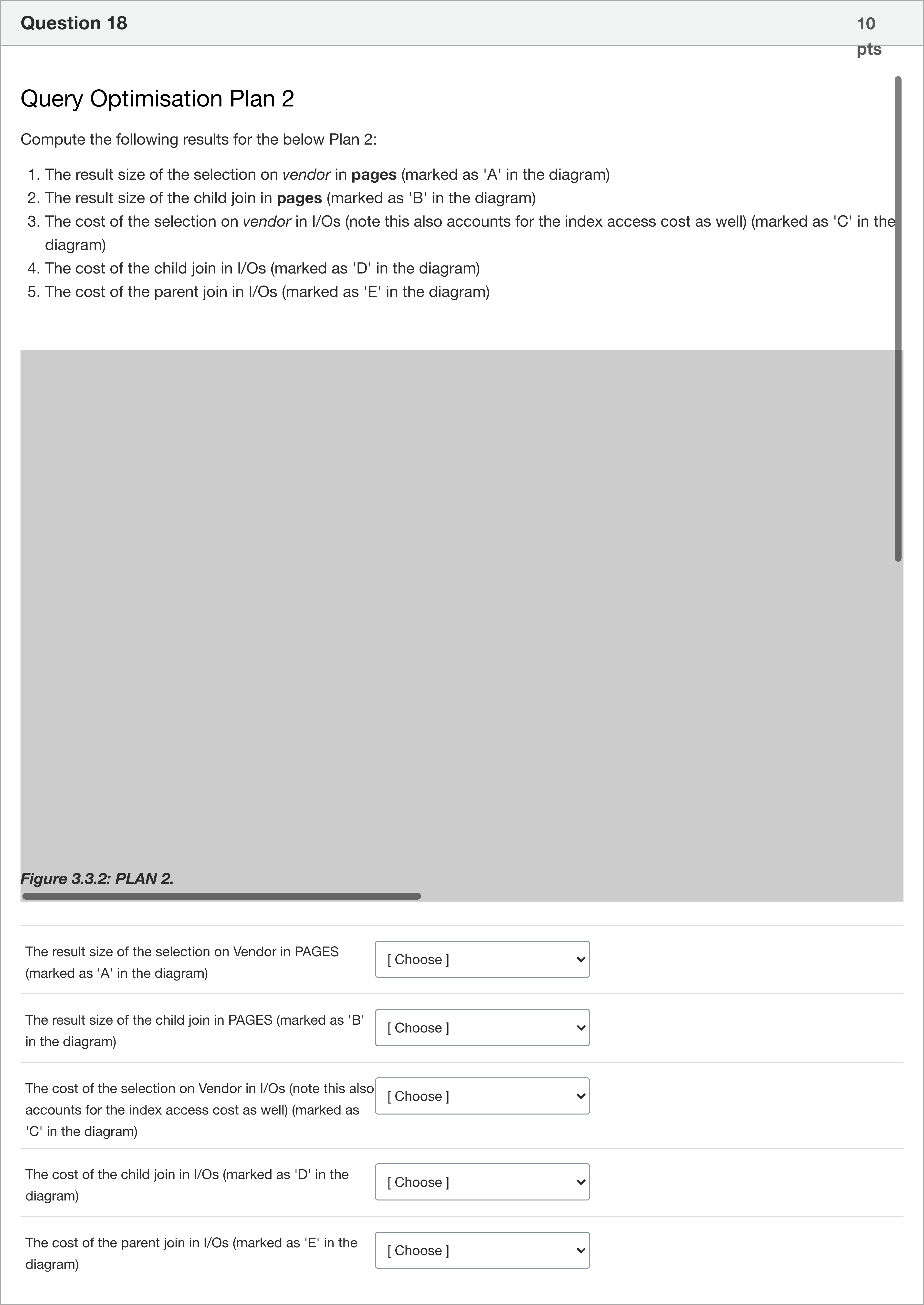
Query Optimisation Plan 2 Compute the following results for the below Plan 2: The result size of the selection on vendor in pages (marked as 'A' in the diagram) The result size of the child join in pages (marked as 'B' in the diagram) The cost of the selection on vendor in I/Os (note this also accounts for the index access cost as well) (marked as 'C' in the diagram) The cost of the child join in I/Os (marked as 'D' in the diagram) The cost of the parent join in I/Os (marked as 'E' in the diagram) Figure 3.3.2: PLAN 2. 1: The result size of the selection on Vendor in PAGES (marked as 'A' in the diagram) 2: The result size of the child join in PAGES (marked as 'B' in the diagram) 3: The cost of the selection on Vendor in I/Os (note this also accounts for the index access cost as well) (marked as 'C' in the diagram) 4: The cost of the child join in I/Os (marked as 'D' in the diagram) 5: The cost of the parent join in I/Os (marked as 'E' in the diagram)
Options
A.500
B.50
C.20,000
D.100
E.105
F.10,000
G.60
H.10,005
I.750
J.5
K.650
L.20,100
M.[Select this if none of the other options are correct]
N.51
O.6
View Explanation
Verified Answer
Please login to view
Step-by-Step Analysis
We are given a matching-type question about Plan 2 in a query optimisation exercise. The prompt asks us to compute five results for Plan 2:
1) The result size of the selection on vendor in pages (A)
2) The result size of the child join in pages (B)
3) The cost of the selection on vendor in I/Os (C)
4) The cost of the child join in I/Os (D)
5) The cost of the parent join in I/Os (E)
The available answer options include a mix of numeric values and a generic placeholder for “none of the others.” The provided answer mapping indicates the intended selections were: A = 5, B = 100, C = 6, D = 10,005, E = 750. Below I’ll analyze each option in turn, noting why a given choice could be plausible and why alternative options would be incorrect.
- Analysis of option choices for A (The result size of the selection on Vendor in PAGES):
• If we consider 5 pages as the result size, this implies a relatively small, highly selective vendor selection after applying an index or predicate. This would be plausible if the vendor relation is large but the selection condition reduces it to only a handful of qualifying rows that aggregate to about 5 pages.
• Why some other options are less suitable: 500, 20,000, 10,000, 650, and 60 pages would imply much larger intermediate results from the vendor selection, which would typically be unlikely if ......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
Query Optimisation Plan 1 Compute the following results for the below Plan 1: The result size of the child join in pages (marked as 'A' in the diagram) The cost of the child join in I/Os (marked as 'B' in the diagram). The cost of the parent join in I/Os (marked as 'C' in the diagram) Figure 3.3.1: PLAN 1. 1: The result size of the child join in PAGES (marked as 'A' in the diagram) 2: The cost of the child join in I/Os (marked as 'B' in the diagram) 3: The cost of the parent join in I/Os (marked as 'C' in the diagram)
Single Relation Plan C What would happen if our query changed and became: SELECT hotspotID FROM hotspot WHERE postcode = 2600 AND establishmentYear > 2020 AND establishmentYear < 2022; Assuming that the unclustered B+tree index on establishmentYear from the previous question is the only index available, would the cost of the best plan change?
Single Relation Plan B Compute the estimated cost of plan alternatives, assuming that an unclustered B+tree index on (establishmentYear) is the only index available. Suppose there are 10 index pages. Give the lowest (estimated) cost in I/Os after considering all access methods available. Round up any decimals to the nearest integer (e.g., 3.3 rounds up to 4).
Single Relation Plan A Compute the estimated result size for the query, and the reduction factor of each filter. 1: RF(establishmentYear) 2: RF(postcode) 3: Result Size (tuples)
More Practical Tools for Students Powered by AI Study Helper
Making Your Study Simpler
Join us and instantly unlock extensive past papers & exclusive solutions to get a head start on your studies!