Questions
AP Economics-Hillebrand Quiz Micro 6.1-6.3- Requires Respondus LockDown Browser
Single choice
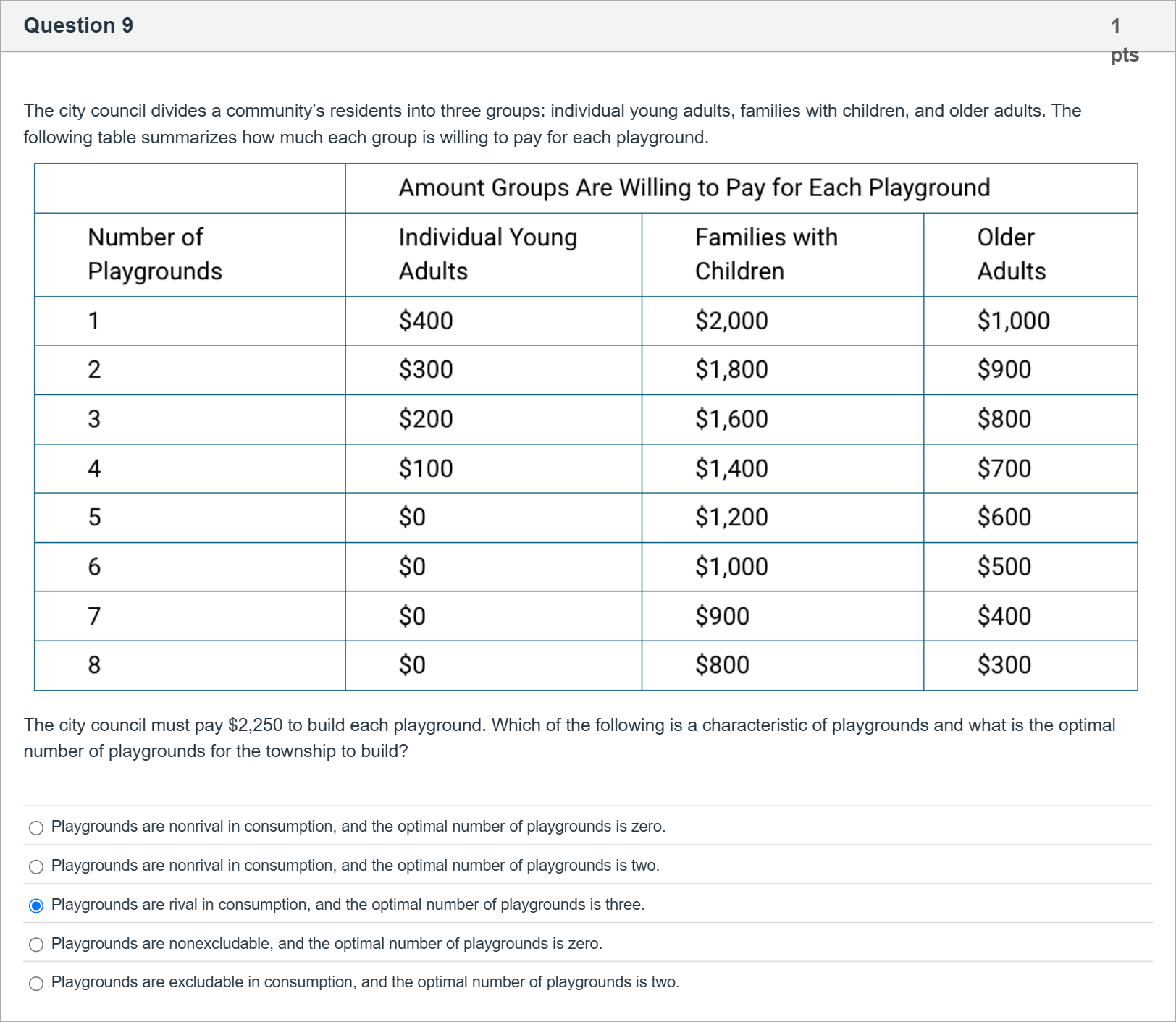
The city council divides a community’s residents into three groups: individual young adults, families with children, and older adults. The following table summarizes how much each group is willing to pay for each playground. The city council must pay $2,250 to build each playground. Which of the following is a characteristic of playgrounds and what is the optimal number of playgrounds for the township to build?
Options
A.Playgrounds are nonrival in consumption, and the optimal number of playgrounds is zero.
B.Playgrounds are nonrival in consumption, and the optimal number of playgrounds is two.
C.Playgrounds are rival in consumption, and the optimal number of playgrounds is three.
D.Playgrounds are nonexcludable, and the optimal number of playgrounds is zero.
E.Playgrounds are excludable in consumption, and the optimal number of playgrounds is two.
View Explanation
Verified Answer
Please login to view
Step-by-Step Analysis
The situation describes a city deciding how many playgrounds to build, given how much each group is willing to pay for each playground and a fixed cost per playground.
Option 1: 'Playgrounds are nonrival in consumption, and the optimal number of playgrounds is zero.' If playgrounds are nonrival (they don’t reduce others’ enjoyment) this is a standard public goods type, but zero is not optimal here because the total willingness to pay for at least one playground exceeds the cost per playground, so at least one would be justified.
O......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
Private supply of public goods is most likely to result in
Question35 Which of the following is an example of non-rival and non-excludable good? National defense Cinemas Paid parking space Fish in the ocean ResetMaximum marks: 1 Flag question undefined
12. The U.S. government built and runs the Smithsonian Museums in Washington, D.C. Admission to all of the museums is free. We can conclude that: A. There is a principal-agent problem. B. Special interests engaged in rent-seeking behavior. C. Private enterprise wouldn’t have provided the free service. D. There is regulatory capture.
3. A demand curve for a public good is determined by: A. summing vertically the individual demand curves for the public good. B. summing horizontally the individual demand curves for the public good. C. combining the amounts of the public good that the individual members of society demand at each price. D. multiplying the per-unit cost of the public good by the quantity made available.
More Practical Tools for Students Powered by AI Study Helper
Making Your Study Simpler
Join us and instantly unlock extensive past papers & exclusive solutions to get a head start on your studies!