Questions
2025FA CSC-239-01H Assessment 2
Single choice
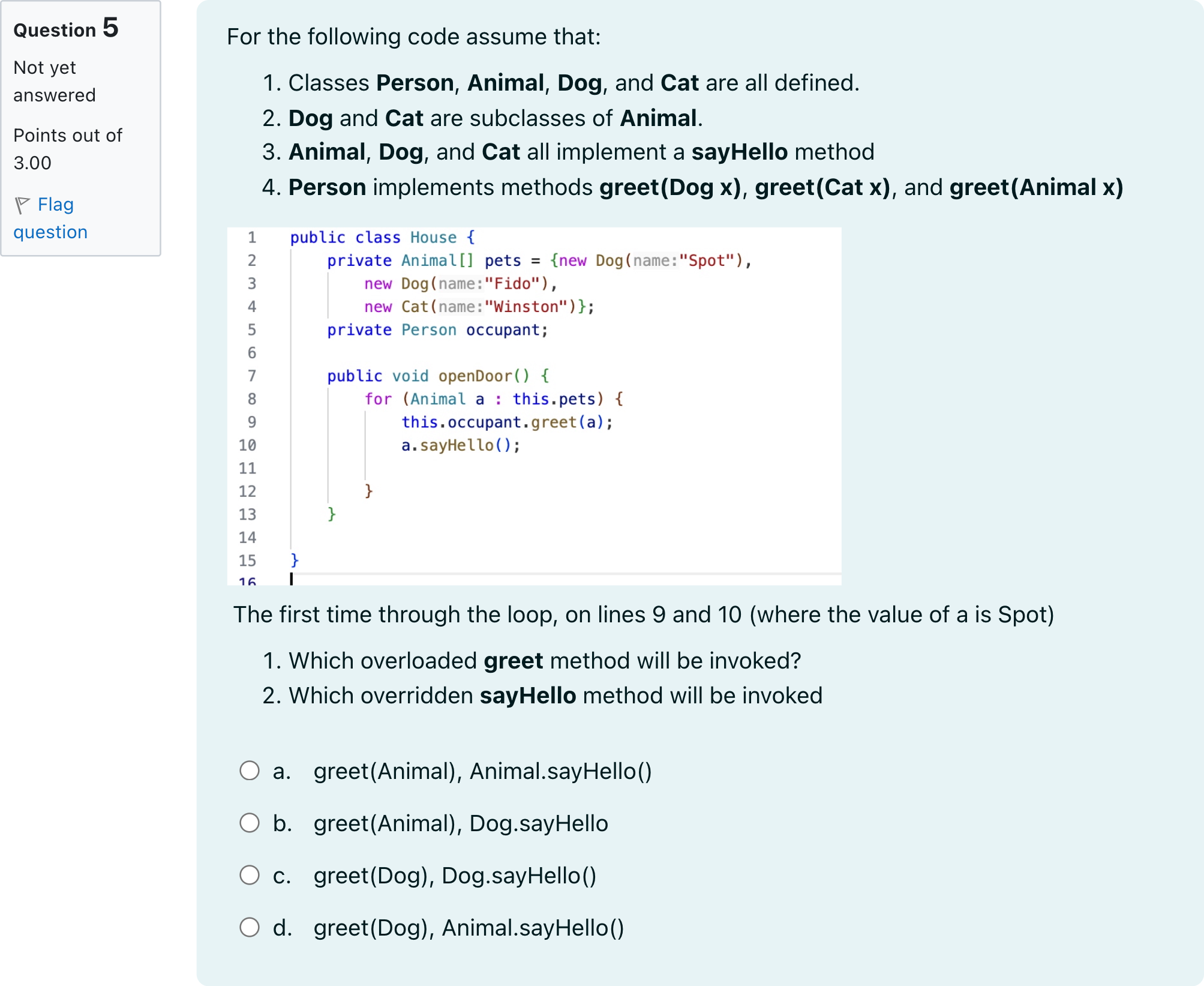
For the following code assume that: Classes Person, Animal, Dog, and Cat are all defined. Dog and Cat are subclasses of Animal. Animal, Dog, and Cat all implement a sayHello method Person implements methods greet(Dog x), greet(Cat x), and greet(Animal x) The first time through the loop, on lines 9 and 10 (where the value of a is Spot) Which overloaded greet method will be invoked? Which overridden sayHello method will be invoked
Options
A.a. greet(Animal), Animal.sayHello()
B.b. greet(Animal), Dog.sayHello
C.c. greet(Dog), Dog.sayHello()
D.d. greet(Dog), Animal.sayHello()
View Explanation
Verified Answer
Please login to view
Step-by-Step Analysis
First, restate what the question is asking: when the loop runs for the first element a (which is a Dog named Spot), which overloaded greet method in Person is chosen, and which overridden sayHello method on the dog is invoked?
Option a: greet(Animal), Animal.sayHello()
- Why this might seem plausible: the for-each iterates with a type of Animal (the array is Animal[]), so at first glance the compiler could pick greet(Animal x).
- Why it’s incorrect: Although the sta......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
Question at position 19 Which of the following demonstrates polymorphism?Overloading methods with different parametersUsing the private keywordDeclaring all methods as staticExtending a class without adding any new methodsClear my selection
Question at position 7 In Java, what must be true for polymorphism to occur during runtime?Method overriding in subclassesClasses must not extend other classesMethod overloading in the parent classVariables declared as protectedClear my selection
Question at position 5 Which one of the following is a correct example of "polymorphism"?Combining two classes into oneUsing different method names for the same or similar actionUsing many classes without any methodsUsing the same method name for similar actions, sometimes even across different classesClear my selection
Question textFor this programming question, you will be working with Polymorphism. Given the base abstract class "airplane", the derived classes "passenger" and "cargo", and the container class "airport" (defined in airport.h): #ifndef AIRPORT_H#define AIRPORT_H #include "airplane.h"#include "passenger.h"#include "cargo.h" #include <vector>#include <string> using namespace std; class airport{private: string city; string code; vector<airplane *> airplanes; public: airport(const string &_city, const string &_code); airport(const airport &RHS); airport &operator=(const airport &RHS); ~airport(); void add_airplane(const airplane &plane); void summary() const; void list_airplanes() const;}; #endif Modify the base class airplane and the derived classes passenger and cargo (following the comments in the provided template files), and write the implementation of the member functions summary and list_airplanes. Here is the implementation of the other member functions of the "airport" class: airport::airport(const string &_city, const string &_code){ city = _city; code = _code;} airport::airport(const airport &RHS){ city = RHS.city; code = RHS.code; for (airplane *plane : RHS.airplanes) { if (plane != nullptr) { airplane *temp_plane; if (plane->get_type() == 'P') { temp_plane = new passenger(*((passenger *)plane)); } else { temp_plane = new cargo(*((cargo *)plane)); } airplanes.push_back(temp_plane); } }} airport &airport::operator=(const airport &RHS){ if (this != &RHS) { city = RHS.city; code = RHS.code; if (airplanes.size() > 0) // Delete allocated memory { for (int i = airplanes.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (airplanes.at(i) != nullptr) { delete airplanes.at(i); airplanes.pop_back(); } } } for (airplane *plane : RHS.airplanes) { if (plane != nullptr) { airplane *temp_plane; if (plane->get_type() == 'P') { temp_plane = new passenger(*((passenger *)plane)); } else { temp_plane = new cargo(*((cargo *)plane)); } airplanes.push_back(temp_plane); } } } return *this;} airport::~airport(){ if (airplanes.size() > 0) // Delete allocated memory { for (int i = airplanes.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (airplanes.at(i) != nullptr) { delete airplanes.at(i); airplanes.pop_back(); } } }} void airport::add_airplane(const airplane &plane){ airplane *temp_plane; if (plane.get_type() == 'P') { temp_plane = new passenger((const passenger &)plane); } else { temp_plane = new cargo((const cargo &)plane); } airplanes.push_back(temp_plane);} HINT: You can use the code from these functions when writing the solution for the requested member functions. NOTES: You can safely assume that the input is always correct. You must use function identifiers based on the specifications of the question when writing your solution. You do not need to write a main function. Solutions that do not compile will receive a 100 % penalty. Hardcoding the output will translate into a 100 % penalty. Answer:(penalty regime: 0 %)// In airport.cpp #include "airport.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; void airport::summary() const { int num_passenger = 0, num_cargo = 0; for (size_t Code for airplane.h 7891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738 int num_passenger = 0, num_cargo = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < airplanes.size(); ++i) { if (airplanes[i]) { if (airplanes[i]->get_type() == 'P') num_passenger++; else if (airplanes[i]->get_type() == 'C') num_cargo++; } } cout << "Airport city: " << city << endl; cout << "Airport code: " << code << endl; cout << "# Passenger airplanes: " << num_passenger << endl; cout << "# Cargo airplanes: " << num_cargo << endl;}void airport::list_airplanes() const { cout << "Passenger airplanes:" << endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < airplanes.size(); ++i) { if (airplanes[i] && airplanes[i]->get_type() == 'P') { airplanes[i]->print(); } } cout << "Cargo airplanes:" << endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < airplanes.size(); ++i) { if (airplanes[i] && airplanes[i]->get_type() == 'C') { airplanes[i]->print(); } }}// airplane.h#ifndef AIRPLANE_H ההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Code for passenger.h 123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536#ifndef PASSENGER_H#define PASSENGER_H#include "airplane.h"#include <iostream>#include <string>using namespace std;// Implement public inheritance from the airplane class// Call the overloaded constructor of the base class in the class overloaded constructor// Use the virtual qualifier when neededclass passenger // Implement public inheritance from the airplane class { private: string airline; int n_passengers; public: passenger(const string & _manufacturer, const string & _model, const string & _tail_number, const string & _airline, int _n_passengers): // Call the overloaded constructor of the base class here { airline = _airline; n_passengers = _n_passengers; } ~passenger(){} char get_type() const {return 'P';} void print() const { airplane::print(); cout << ", Airline: " << airline << ", # of passengers: " << n_passengers << endl; }};#endif ההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Code for cargo.h 1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435#ifndef CARGO_H#define CARGO_H#include "airplane.h"#include <iostream>using namespace std;// Implement public inheritance from the airplane class// Call the overloaded constructor of the base class in the class overloaded constructor// Use the virtual qualifier when neededclass cargo // Implement public inheritance from the airplane class { private: string company; int max_capacity; public: cargo(const string & _manufacturer, const string & _model, const string & _tail_number, const string & _company, int _max_capacity): // Call the overloaded constructor of the base class here { company = _company; max_capacity = _max_capacity; } ~cargo(){} char get_type() const {return 'C';} void print() const { airplane::print(); cout << ", Company: " << company << ", Max Capacity (tons): " << max_capacity << endl; }};#endif ההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Code for airport.cpp 12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849505152// Include the libraries to run compile your solution#include "airport.h"#include <iostream>using namespace std;// Write the implementation of the requested member functions void airport::summary const{ int num_passenger = 0, num_cargo = 0; for (size_t i=0, i < airplanes.size(); ++i) { if (airplane[i]) { if (airplane[i]) get_type() - > == 'P' num_passenger ++; else (airplane[i]) get_type() - > == "C" num_cargo ++; } cout <<"Airport city: " << city << endl; cout <<"Airport code: " << code << endl; cout <<"# Passeneger airplanes:" << num_passenger << endl; cout <<"# Cargo airplanes:" << num_cargo << endl;}void airport::list_airplane() const{ cout <<"Passenger airplanes:" endl; for (size_t i=0 i < airplane.size(); ++1 { if (airplane[i] && airplane[i] - > get_type() == 'P') airplane[i]- > print(); } cout <<"Cargo airplanes:" << endl; for (size_t i=0, i < airplanes.size(); ++1) { if (airplane[i] && airplane[i] - > get_type() == 'C') airplane[i] - > print(); }}// Output messages for the summary function// cout << "Airport city: " << /* variable identifier */ << endl;// cout << "Airport code: " << /* variable identifier */ << endl;// cout << "# Passenger airplanes: " << /* variable identifier */ << endl;// cout << "# Cargo airplanes: " << /* variable identifier */ << endl;// Output messages for the list_airplanes function// cout << "Passenger airplanes: " << endl;// cout << "Cargo airplanes: " << endl; ההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההההXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX M.util.js_pending('qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'); require(['qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'], function(amd) { amd.newUiWrapper("ace", "id_q55064:2_answer-ace_field1"); M.util.js_complete('qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'); }); M.util.js_pending('qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'); require(['qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'], function(amd) { amd.newUiWrapper("ace", "id_q55064:2_answer-ace_field2"); M.util.js_complete('qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'); }); M.util.js_pending('qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'); require(['qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'], function(amd) { amd.newUiWrapper("ace", "id_q55064:2_answer-ace_field3"); M.util.js_complete('qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'); }); M.util.js_pending('qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'); require(['qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'], function(amd) { amd.newUiWrapper("ace", "id_q55064:2_answer-ace_field4"); M.util.js_complete('qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'); }); Check Question 1
More Practical Tools for Students Powered by AI Study Helper
Making Your Study Simpler
Join us and instantly unlock extensive past papers & exclusive solutions to get a head start on your studies!