Questions
AGRI30048_2025_SM2 Practice Questions for the Mid Semester Test - UNMARKED REVISION QUESTIONS
Essay
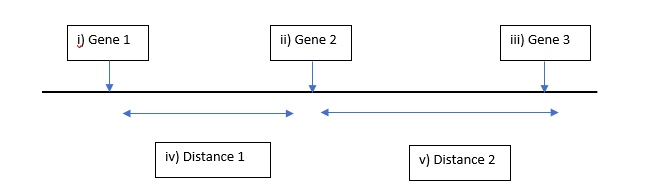
In a Test cross data of tomato, in which the heterozygous F1 plants were crossed with a strain that has ovate fruit, curled leaves and mottled coloration (homozygous recessive ovov cucu momo), the following progeny were observed: Normal curled mottled 3 A Normal curled solid 26 B Normal flat solid 304 C Normal flat mottled 68 D Ovate curled mottled 310 E Ovate curled solid 60 F Ovate flat mottled 24 G Ovate flat solid 5 H Note: Normal fruit vs. ovate fruit Flat leaves or curled leaves Solid color or mottled coloration a) List the two parental genotypes of the original cross that produced the F1. b) Designate the parental, single crossover, and double crossover classes of offspring. (Label each row of the above list: as parental, single crossover, or double crossover class of offspring. (Answer the question by giving your answers for each from A-H or copy and paste the table in the answer box). c) Determine the order of gene loci and calculate the genetic distance of these three loci. Include calculation details. Present the data as a labeled linkage map. Drawing of the linkage map can be provided either as an uploaded document or the answers can be given for the boxes as labeled i) to v) in the following image.
View Explanation
Verified Answer
Please login to view
Step-by-Step Analysis
The question presents a test-cross in tomato where heterozygous F1 plants were crossed to a homozygous recessive line with ovate fruit, curled leaves, and mottled coloration. The observed progeny are grouped by three traits: fruit shape (Normal vs Ovate), leaf type (flat vs curled), and coloration (solid vs mottled). The task has three parts: (a) identify the original parental genotypes, (b) classify each progeny class as parental, single cross over (SCO), or double cross over (DCO), and (c) determine gene order and map distances.
Option a) “The original cross must have been between a homozygous dominant (Normal fruit, flat leaves, solid color: OVOV CuCu MoMo) and a homozygous recessive (ovov cucu momo). The F1 plants are all heterozygous for the dominant traits: Ov ov Cu cu Mo mo.”
- This analysis correctly recognizes that the F1 must be heterozygous for the three loci if the cross involved a dominant-phenotype homozygous parent with a recessive-phenotype homozygous parent. However, the stated genotypes mix case conventions and notation inconsistencies (OVOV CuCu MoMo vs Ov ov Cu cu Mo mo) which can be confusing. The essential idea—two homozygous parents, one with dominant phenotypes and one with recessive phenotypes, producing a heterozygous F1—is sound. A more precise statement would specify that the dominant-phenotype parent carries alleles in coupling (e.g., Fruit shape Normal......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
In a consumer society, many adults channel creativity into buying things
Economic stress and unpredictable times have resulted in a booming industry for self-help products
People born without creativity never can develop it
A product has a selling price of $20, a contribution margin ratio of 40% and fixed cost of $120,000. To make a profit of $30,000. The number of units that must be sold is: Type the number without $ and a comma. Eg: 20000
More Practical Tools for Students Powered by AI Study Helper
Making Your Study Simpler
Join us and instantly unlock extensive past papers & exclusive solutions to get a head start on your studies!