Questions
INEF001 Assessment Quiz 2 - Requires Respondus LockDown Browser
Short answer
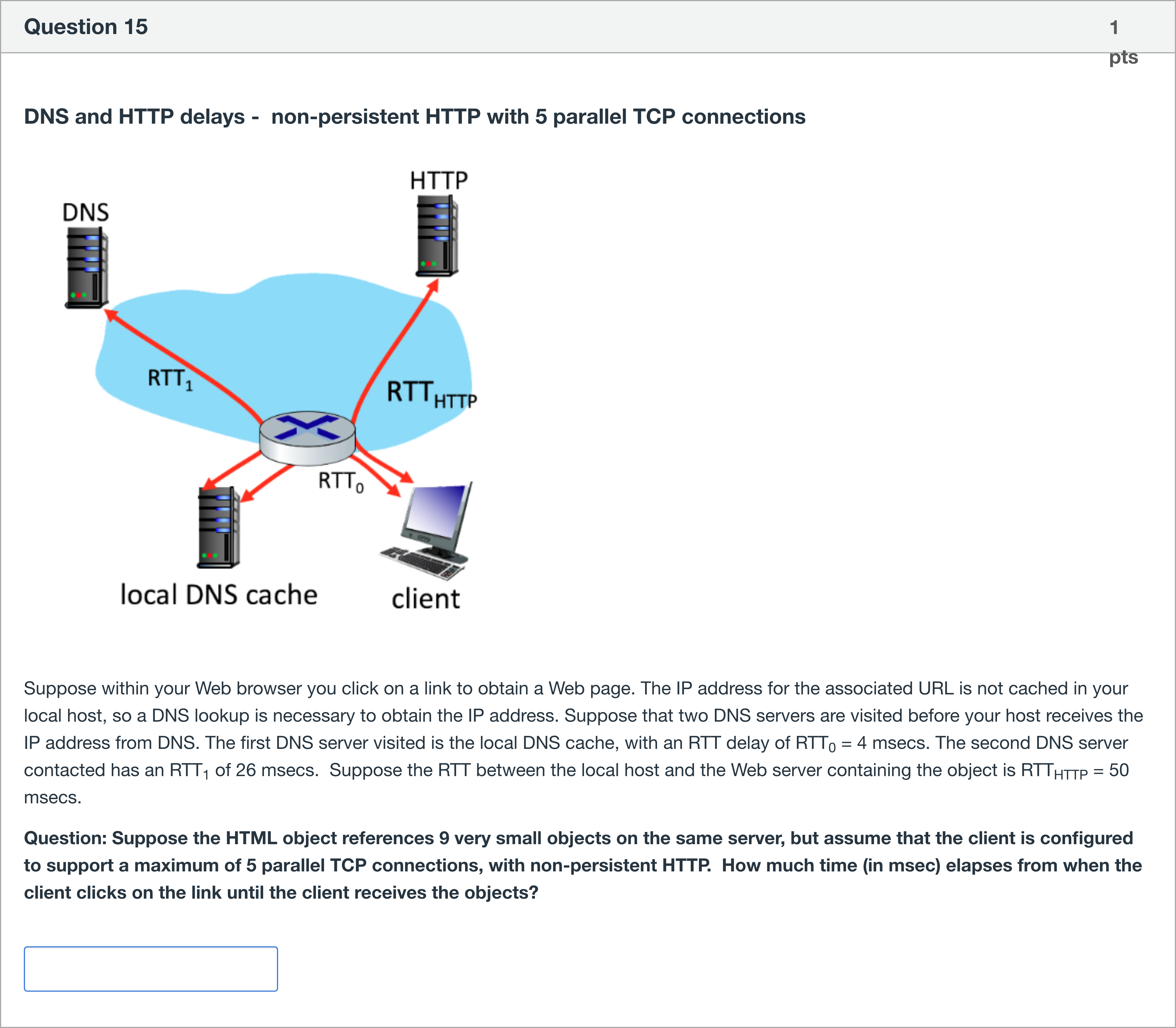
DNS and HTTP delays - non-persistent HTTP with 5 parallel TCP connections Suppose within your Web browser you click on a link to obtain a Web page. The IP address for the associated URL is not cached in your local host, so a DNS lookup is necessary to obtain the IP address. Suppose that two DNS servers are visited before your host receives the IP address from DNS. The first DNS server visited is the local DNS cache, with an RTT delay of RTT0 = 4 msecs. The second DNS server contacted has an RTT1 of 26 msecs. Suppose the RTT between the local host and the Web server containing the object is RTTHTTP = 50 msecs. Question: Suppose the HTML object references 9 very small objects on the same server, but assume that the client is configured to support a maximum of 5 parallel TCP connections, with non-persistent HTTP. How much time (in msec) elapses from when the client clicks on the link until the client receives the objects?
View Explanation
Verified Answer
Please login to view
Step-by-Step Analysis
To solve this, we need to break the total delay into two parts: DNS resolution time and the time to fetch all the HTTP objects.
- DNS resolution: The browser must perform two DNS lookups. The first is the local DNS cache with RTT0 = 4 ms, and the second goes to another DNS server with RTT1 = 26 ms. The total DNS time is RTT0 + RTT1 = 4 + 26 = 30 ms.
- HTTP object fetches: After DNS, the HTML object references 9 very small objects on the same server. The client is configured to......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
In a consumer society, many adults channel creativity into buying things
Economic stress and unpredictable times have resulted in a booming industry for self-help products
People born without creativity never can develop it
A product has a selling price of $20, a contribution margin ratio of 40% and fixed cost of $120,000. To make a profit of $30,000. The number of units that must be sold is: Type the number without $ and a comma. Eg: 20000
More Practical Tools for Students Powered by AI Study Helper
Making Your Study Simpler
Join us and instantly unlock extensive past papers & exclusive solutions to get a head start on your studies!