Questions
AVBS2001 (ND) Prep for Microscopy Prac 2 in week 3 (1%): Disorders of Growth and Circulatory
Multiple dropdown selections
The best place to view the primary pathological process in action is generally on the edge of the lesion- in the middle it will often be confused by secondary changes, such as necrosis and haemorrhage. Normal lung to left of image. On right note infiltration of alveolar spaces by cells. Note different sizes and shapes of cells (pleiomorphism), some binucleated cells, some joined and others not (degrees of de-differentiation) Name the labels for the section below: A: Alveolar wall , B: Cells forming a line , C: Cells within alveolar spaces .
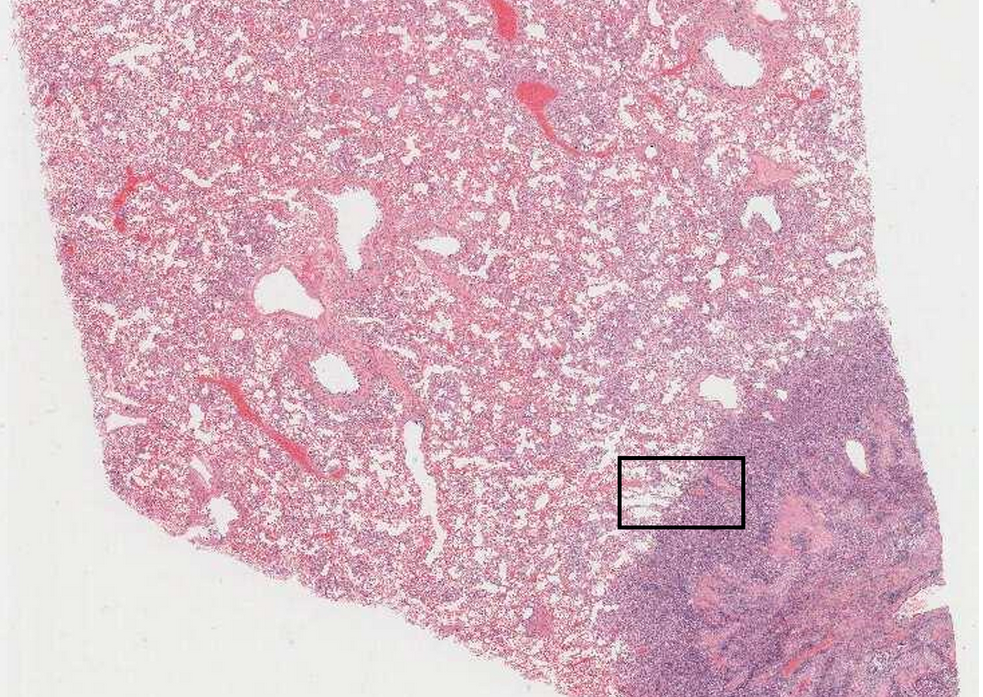
View Explanation
Verified Answer
Please login to view
Step-by-Step Analysis
To approach this question, we first restate what is being asked and what each label is supposed to identify in the histology image.
- A: Alveolar wall
- B: Cells forming a line
- C: Cells within alveolar spaces
Option 1 (A: Alveolar wall) analysis:
The alveolar walls (septae) are the structural partitions between adjacent alveoli. In many lung pathology images, primary processes such as inflammatory or neoplastic changes can be most evident at the edge of a lesion where the architecture is disrupted but not yet overwhelmed by secondary changes. If the box in the image is highlighting tissue at the thin connec......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
Question at position 20 Which one of the following requires magnification to study? Histology Regional anatomy Gross anatomy Surface anatomy
In the colon, the muscularis externa is primarily composed of Blank 1 Question 17[select: , skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, dense connective tissue, lamina propria] , while the mucosal epithelium consists of Blank 2 Question 17[select: , stratified cuboidal, simple squamous, simple columnar, stratified squamous] cells.
In one area, there is a raised, dome-like lesion. The mass is well demarcated and doesn’t extend into the subcutis. The lesion is covered by a thin layer of epidermis, which has become ulcerated and shows superficial infiltration by individual round cells with a lobulated nucleus (neutrophils) and plump spindle-shaped mesenchymal cells (likely fibroblasts and vascular endothelial cells in repair). Label the features: A: Mesenchymal cells (fibroblasts or endothelial cells) , B: Neutrophils , C: Collagen Fibres
Name the endocrine organ featured in this micrograph (histological image)
More Practical Tools for Students Powered by AI Study Helper
Making Your Study Simpler
Join us and instantly unlock extensive past papers & exclusive solutions to get a head start on your studies!