Questions
BIOL3612.MERGED.202610 Activity Questions from the Literature 2B: Preparing tRNAs and synthesizing protein
Single choice
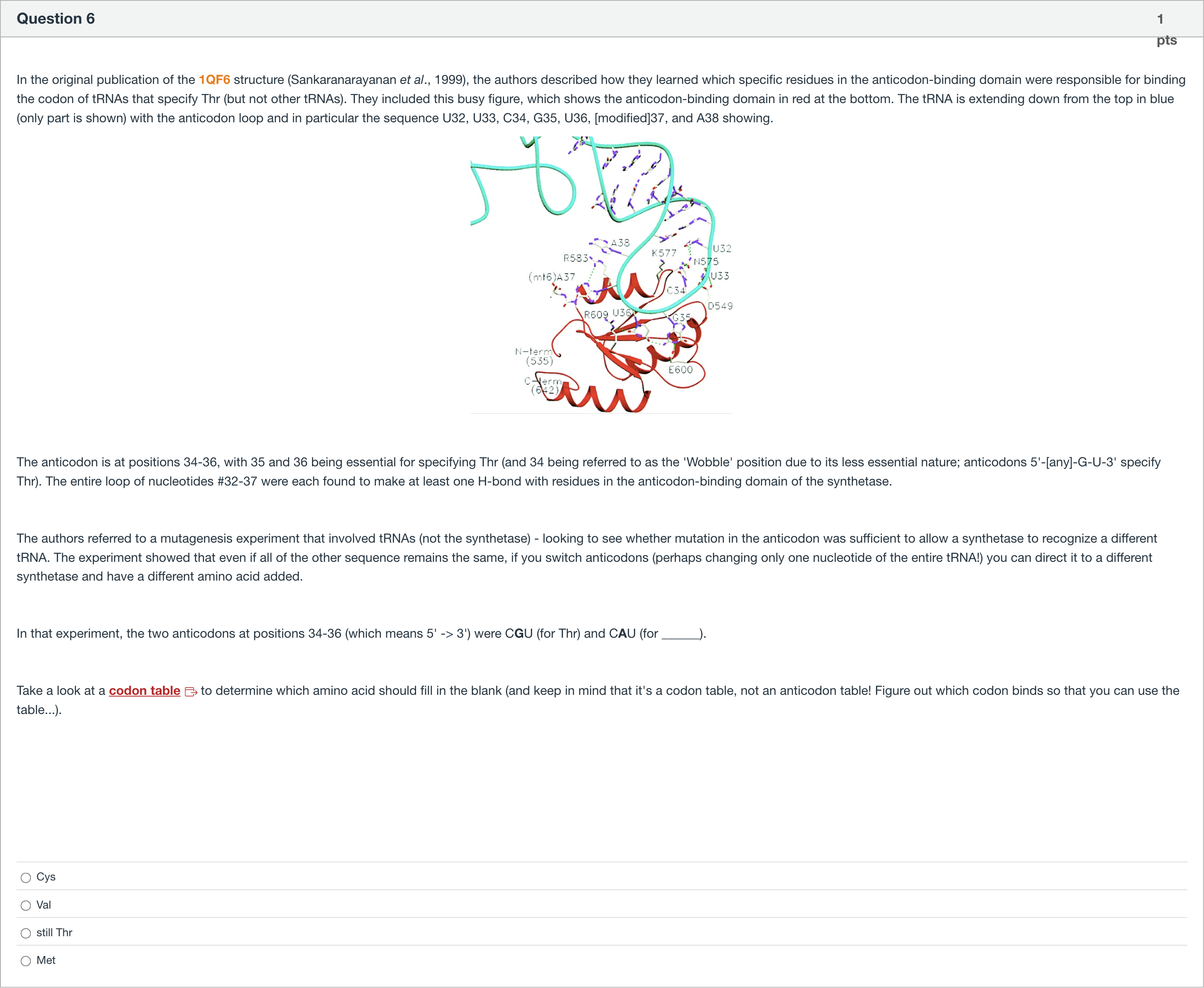
In the original publication of the 1QF6 structure (Sankaranarayanan et al., 1999), the authors described how they learned which specific residues in the anticodon-binding domain were responsible for binding the codon of tRNAs that specify Thr (but not other tRNAs). They included this busy figure, which shows the anticodon-binding domain in red at the bottom. The tRNA is extending down from the top in blue (only part is shown) with the anticodon loop and in particular the sequence U32, U33, C34, G35, U36, [modified]37, and A38 showing. The anticodon is at positions 34-36, with 35 and 36 being essential for specifying Thr (and 34 being referred to as the 'Wobble' position due to its less essential nature; anticodons 5'-[any]-G-U-3' specify Thr). The entire loop of nucleotides #32-37 were each found to make at least one H-bond with residues in the anticodon-binding domain of the synthetase. The authors referred to a mutagenesis experiment that involved tRNAs (not the synthetase) - looking to see whether mutation in the anticodon was sufficient to allow a synthetase to recognize a different tRNA. The experiment showed that even if all of the other sequence remains the same, if you switch anticodons (perhaps changing only one nucleotide of the entire tRNA!) you can direct it to a different synthetase and have a different amino acid added. In that experiment, the two anticodons at positions 34-36 (which means 5' -> 3') were CGU (for Thr) and CAU (for ______). Take a look at a codon table Links to an external site. to determine which amino acid should fill in the blank (and keep in mind that it's a codon table, not an anticodon table! Figure out which codon binds so that you can use the table...).
Options
A.Cys
B.Val
C.still Thr
D.Met
View Explanation
Verified Answer
Please login to view
Step-by-Step Analysis
To approach this question, we need to connect the anticodon mutations to the codon table and determine which amino acid corresponds to the codon formed by the anticodon CGU (Thr) and CAU (the other anticodon in question).
Option 1: Cys. This would imply that switching the anticodon from CGU to CAU redirected the tRNA to be charged with cysteine. However, the codons encoding cysteine are UGU and UGC in the standard genetic code, which do not match the CAU anticodon pairing pattern described here. Therefore, this choice misaligns with the codon table.
Option 2: Val. If the ......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
Question at position 72 True or False. The genetic code in bacteria is different from the genetic code in humans.TrueFalse
Question at position 28 Select all of the attributes of the genetic code.Codons do not overlapEvery codon codes for an amino acidCodons do overlapThe genetic code is not redundantEvery codon is usedThe genetic code is redundant
Question at position 5 True or False. The stop codons code for Trp.TrueFalse
A codon is composed of
More Practical Tools for Students Powered by AI Study Helper
Making Your Study Simpler
Join us and instantly unlock extensive past papers & exclusive solutions to get a head start on your studies!