Questions
ECN 001B B01-B04 FQ 2025 Final Examination
Single choice
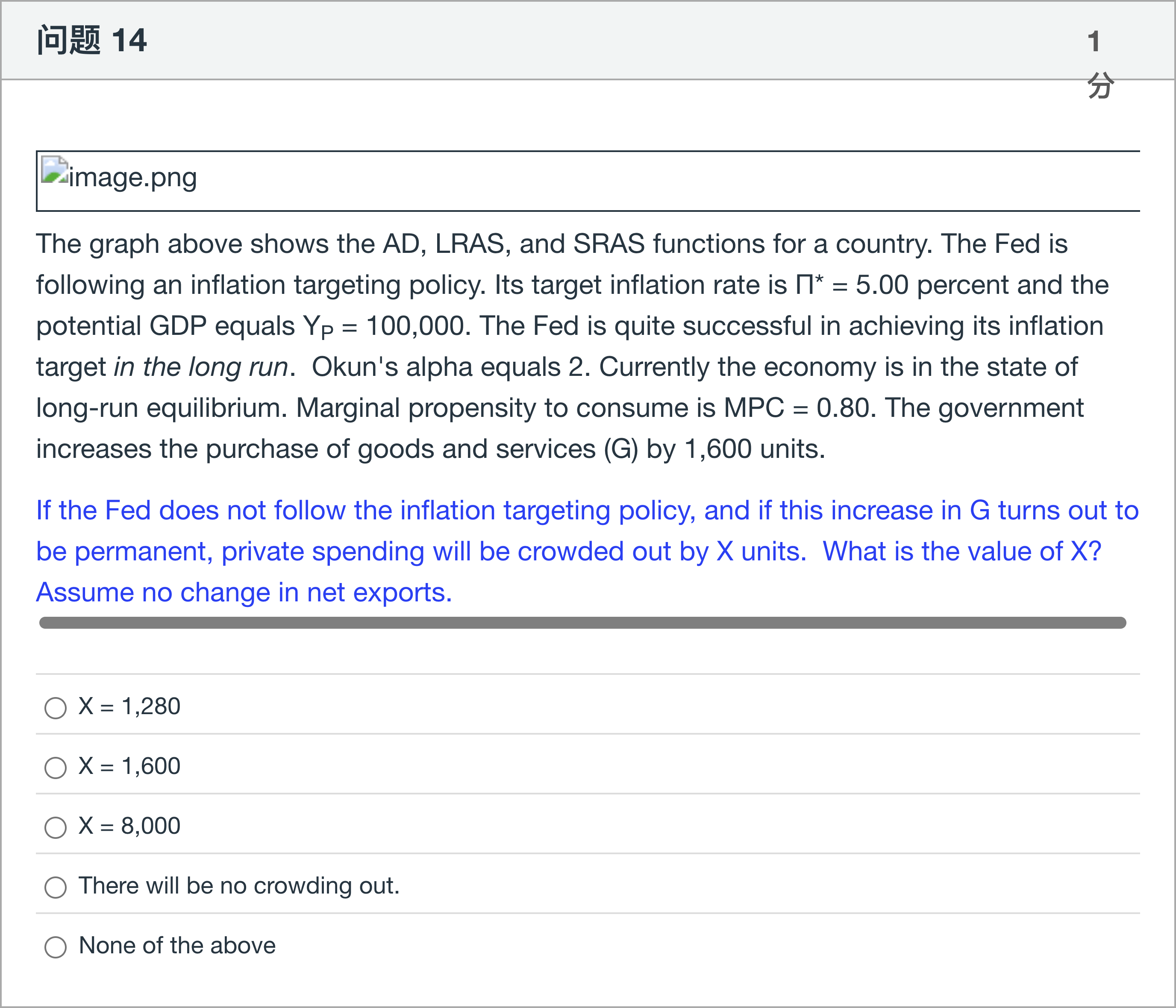
The graph above shows the AD, LRAS, and SRAS functions for a country. The Fed is following an inflation targeting policy. Its target inflation rate is Π* = 5.00 percent and the potential GDP equals YP = 100,000. The Fed is quite successful in achieving its inflation target in the long run. Okun's alpha equals 2. Currently the economy is in the state of long-run equilibrium. Marginal propensity to consume is MPC = 0.80. The government increases the purchase of goods and services (G) by 1,600 units. If the Fed does not follow the inflation targeting policy, and if this increase in G turns out to be permanent, private spending will be crowded out by X units. What is the value of X? Assume no change in net exports.
Options
A.X = 1,280
B.X = 1,600
C.X = 8,000
D.There will be no crowding out.
E.None of the above
View Explanation
Verified Answer
Please login to view
Step-by-Step Analysis
We start by parsing the scenario and the numbers given. The model specifies: MPC = 0.80, government spending (G) increases by 1,600 units, and we are told to assume no change in net exports and a permanent change in G under a regime where the Fed does not pursue its inflation target. The question asks for the amount by which private spending is crowded out, X, when this permanent increase in G occurs.
First, consider the standard spending multiplier that relates a change in autonomous spending to the change in output in the short run (or in a simple Keynesian framework):
- Multiplier k = 1 / (1 – MPC) = 1 / (1 – 0.80) = 1 / 0.20 = 5.
- If there were no crowding out at all, a 1,600 increase in G would generate an aggregate demand increase of ΔY = k × ΔG = 5 × 1,600 = 8,000.
Next, tr......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
Fiscal policy refers to the idea that changes in:
Consider the following graph. Suppose the economy is currently at a point like A. Assume the central bank in this economy remains idle. What type of policy can the Government conduct to reach point B?
______________ are changes in federal taxes and government purchases that are intended to achieve macroeconomic policy goals, and ______________ are changes in federal taxes and government spending that respond to the Business Cycle without direct government action.
Which of the following has been cited by economists as a drawback of fiscal policy in comparison to monetary policy?
More Practical Tools for Students Powered by AI Study Helper
Making Your Study Simpler
Join us and instantly unlock extensive past papers & exclusive solutions to get a head start on your studies!