Questions
Multiple fill-in-the-blank
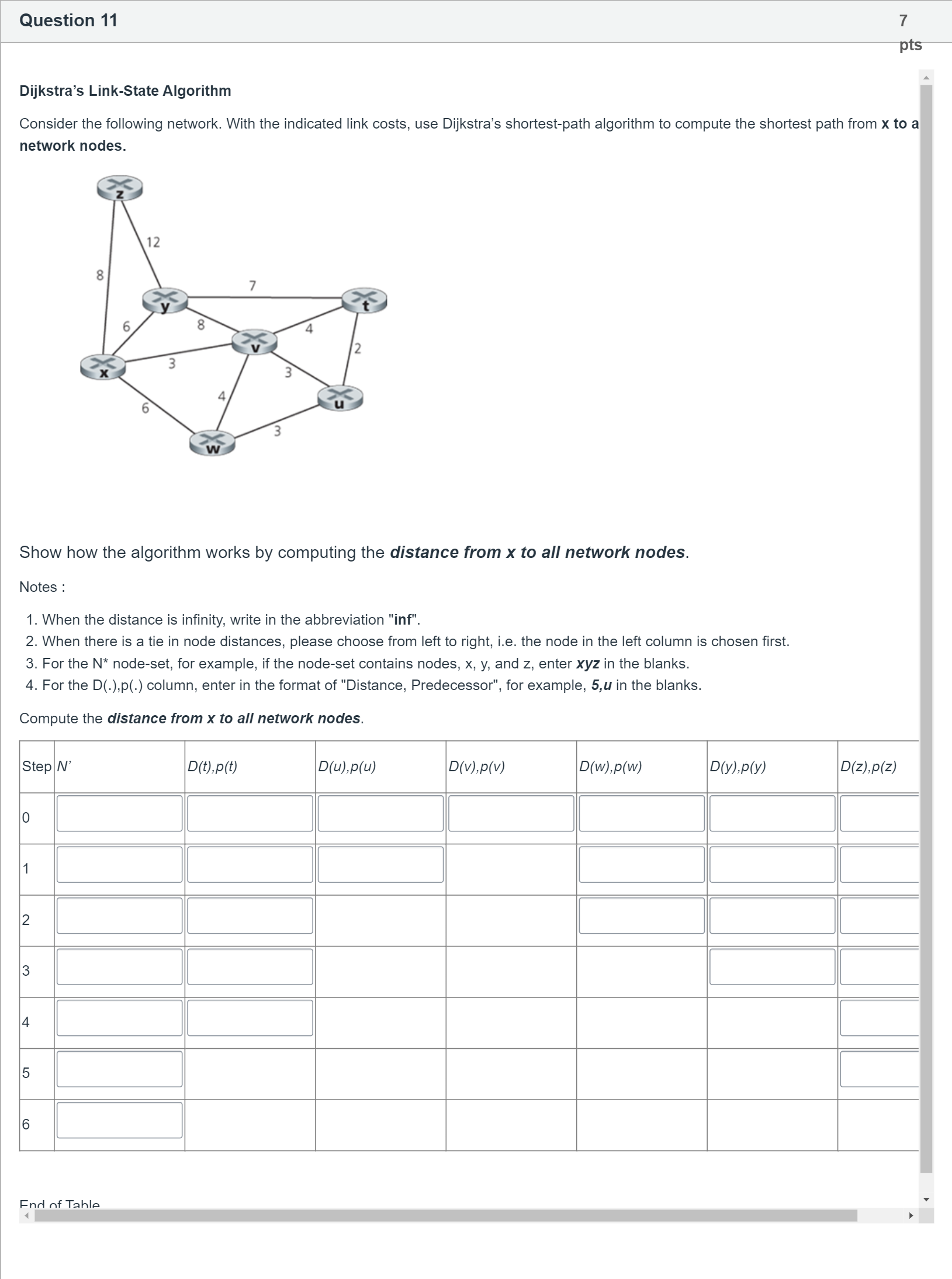
Dijkstra’s Link-State Algorithm Consider the following network. With the indicated link costs, use Dijkstra’s shortest-path algorithm to compute the shortest path from x to all network nodes. Show how the algorithm works by computing the distance from x to all network nodes. Notes : When the distance is infinity, write in the abbreviation "inf". When there is a tie in node distances, please choose from left to right, i.e. the node in the left column is chosen first. For the N* node-set, for example, if the node-set contains nodes, x, y, and z, enter xyz in the blanks. For the D(.),p(.) column, enter in the format of "Distance, Predecessor", for example, 5,u in the blanks. Compute the distance from x to all network nodes. Step N’ D(t),p(t) D(u),p(u) D(v),p(v) D(w),p(w) D(y),p(y) D(z),p(z) 0 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] 1 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] 2 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] 3 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] 4 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] 5 [Fill in the blank] [Fill in the blank] 6 [Fill in the blank] End of Table
View Explanation
Verified Answer
Please login to view
Step-by-Step Analysis
Question restatement and data we have:
- The problem asks to apply Dijkstra’s Link-State Algorithm on the provided network, starting from node x, and to compute the distance from x to all network nodes. Infinity is denoted by inf, and ties are resolved left-to-right. For each step, the table requires entries for N’ and for the D(t),p(t) values of each target node (D(u),p(u), D(v),p(v), D(w),p(w), D(y),p(y), D(z),p(z)). These entries are to be filled as the algorithm proceeds, with the format "Distance, Predecessor" (e.g., 5,u).
- The given data include a stepwise structure (Step 0 through Step 6) and a long list of strings in the answer field, which appear to be intended final contents for the multiple blanks in the table, organized in some specific order, but the corresponding answer_options field is empty. This means there are no multiple-choice options to evaluate here; instead, the task is to compute and fill in the table using the Dijkstra process.
Approach to analyze the problem without explicit answer options:
- Clarify the goal: determine the shortest distance from x to every other node in the graph, and als......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
Dijkstra's Link State Algorithm Consider the incomplete 6-node network shown below, with given link costs; where links x and y are unknown Consider the completed table below, which calculates the shortest distance to all nodes from U: Nodes d, (p) d, (p) d, (p) d, (p) d, (p) U V W X Y Z shortest distance from node U 0 4, X 3, U 1, U 5, X 6, W For link x (link from node X, to node Y) , what is the cost associated with this link? [Fill in the blank] For link y (link from node U to node W) , what is the cost associated with this link?[Fill in the blank]
Question at position 4 Which route computation algorithm is used by the OSPF routing mechanism?DijkstraBellman-FordNone of ThemDSR
If Dijkstra's algorithm is performed on the graph with vertex set { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 } and adjacency matrix given below, what is the sequence of edges added to the result (shortest path tree). Use vertex 0 as a source. We break ties between vertices by picking the vertex with lower index. For example, EXTRACT-MIN returns vertex 1 before vertex 2, if both vertices have the same minimum estimate. ( 0 8 5 9 6 3 8 0 2 2 5 2 5 2 0 3 1 7 9 2 3 0 1 9 6 5 1 1 0 9 3 2 7 9 9 0 )
SPath_Alg_1 This question relates to the use of the Graph Abstract Data Type (ADT) implemented with an Adjacency Map, as covered in class. Below is the pseudocode for Dijkstra’s Algorithm: function DijkstraShortestPaths(Graph G, Vertex src): Initialize distance map d ← empty map Initialize visited set cloud ← empty set Initialize priority queue pq Initialize pqLocator ← empty map for each vertex v in G: if v == src: d[v] ← 0 else: d[v] ← ∞ pqLocator[v] ← pq.insert(d[v], v) while pq is not empty: (minDist, u) ← pq.remove_min() cloud[u] ← minDist remove pqLocator[u] for each edge (u, v) incident from u: if v not in cloud: weight ← weight of edge (u, v) if d[u] + weight < d[v]: d[v] ← d[u] + weight pq.update(pqLocator[v], d[v], v) return cloud During the execution of the while loop, under what condition does the algorithm update a vertex v’s distance and modify its position in the priority queue? Graph ADT For reference: class Vertex: def __init__(self, x): self._element = x class Edge: def __init__(self, u, v, x): self._origin = u self._destination = v self._element = x def opposite(self, v): return self._destination if v == self._origin else self._origin class Graph: def __init__(self, directed=False): self._outgoing = {} self._incoming = {} if directed else self._outgoing def incident_edges(self, v): return self._outgoing[v].values()
More Practical Tools for Students Powered by AI Study Helper
Making Your Study Simpler
Join us and instantly unlock extensive past papers & exclusive solutions to get a head start on your studies!