Still overwhelmed by exam stress? You've come to the right place!
We know exam season has you totally swamped. To support your studies, access Gold Membership for FREE until December 31, 2025! Normally £29.99/month. Just Log In to activate – no strings attached.
Let us help you ace your exams efficiently!
Questions
Dashboard Mock Final
Multiple fill-in-the-blank
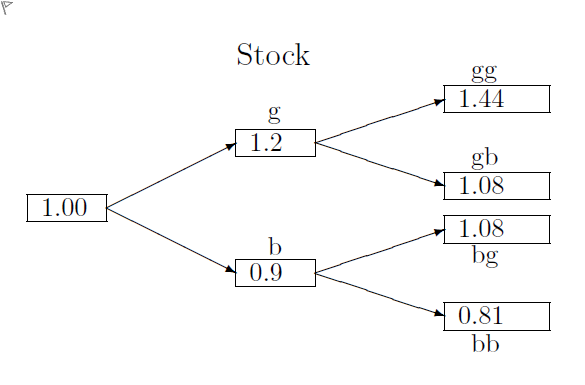
Question textThe following information refers to parts A-B below, select the right answer from the drop-down menu. Consider a three period binomial time-state model in which there are two securities, a bond and a stock. The bond price increases [math: 2%]2\% of its prior value in every period and its initial price is 1. The payments made by the stock are shown in the binomial tree below: The [math: Patom]\mathbf {P_{atom}} vector represents the atomic (time-state) prices of elementary payment for states [math: g], [math: b], [math: gg], [math: gb], [math: bg] and [math: bb], respectively, rounded to 4 decimal digits. [math: Patom=(0.3922,0.5882,0.1538,0.2307,0.2307,?)] \mathbf {P_{atom}}=(0.3922, 0.5882, 0.1538, 0.2307, 0.2307, ?) A) The discount factor of period 1 is: Answer 1 Question 3[select: , 0.30, 0.83, 0.98, 1.94, none of the above] B) The atomic security price of state [math: bb] is equal to: Answer 2 Question 3[select: , 0.1560, 0.2360, 0.2560, 0.3460, 0.4060]
View Explanation
Standard Answer
Please login to view
Approach Analysis
Question restatement:
- We are given a three-period binomial time-state model with a bond that grows by 2% each period and starts at price 1. The stock pays certain amounts shown in the tree, and Patom is the vector of atomic (time-state) prices for the six final states (gg, gb, bg, bb, and their counterparts as listed): Patom = (0.3922, 0.5882, 0.1538, 0.2307, 0.2307, ?). The problem asks:
A) The discount factor of period 1 is which value from: [ , 0.30, 0.83, 0.98, 1.94, none of the above]
B) The atomic security price of state bb is which value from: [ , 0.1560, 0.2360, 0.2560, 0.3460, 0.4060]
Answer given: A = 0.98, B = 0.1560.
Option-by-option reasoning for A (discount factor of period 1):
- Concept to use: If the bond grows by 2% each period, its gross return over one period is 1.02. The corresponding per-period discount factor is the reciprocal of the gross return, which is 1 / 1.02 ≈ 0.98039. This is the present-value multi......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
For some value of p, the payoff associated with node F is 4045.16, and the payoff associated with G is -842.99. What is the payoff associated with node C?
Question textThe following information refers to parts A-B below, select the right answer from the drop-down menu. Consider a three period binomial time-state model in which there are two securities, a bond and a stock. The bond price increases [math: 2%]2\% of its prior value in every period and its initial price is 1. The payments made by the stock are shown in the binomial tree below: The [math: Patom]\mathbf {P_{atom}} vector represents the atomic (time-state) prices of elementary payment for states [math: g], [math: b], [math: gg], [math: gb], [math: bg] and [math: bb], respectively, rounded to 4 decimal digits. [math: Patom=(0.3922,0.5882,0.1538,0.2307,0.2307,?)] \mathbf {P_{atom}}=(0.3922, 0.5882, 0.1538, 0.2307, 0.2307, ?) A) The discount factor of period 1 is: Answer 1 Question 7[select: , 0.30, 0.83, 0.98, 1.94, none of the above] B) The atomic security price of state [math: bb] is equal to: Answer 2 Question 7[select: , 0.1560, 0.2360, 0.2560, 0.3460, 0.4060]
Question textThe following information refers to parts A-B below, select the right answer from the drop-down menu. Consider a three period binomial time-state model in which there are two securities, a bond and a stock. The bond price increases [math: 2%]2\% of its prior value in every period and its initial price is 1. The payments made by the stock are shown in the binomial tree below: The [math: Patom]\mathbf {P_{atom}} vector represents the atomic (time-state) prices of elementary payment for states [math: g], [math: b], [math: gg], [math: gb], [math: bg] and [math: bb], respectively, rounded to 4 decimal digits. [math: Patom=(0.3922,0.5882,0.1538,0.2307,0.2307,?)] \mathbf {P_{atom}}=(0.3922, 0.5882, 0.1538, 0.2307, 0.2307, ?) A) The discount factor of period 1 is: Answer 1 Question 5[select: , 0.30, 0.83, 0.98, 1.94, none of the above] B) The atomic security price of state [math: bb] is equal to: Answer 2 Question 5[select: , 0.1560, 0.2360, 0.2560, 0.3460, 0.4060]
You are operating a gas turbine power station (GTPS). The risk factor driving cash inflows (revenues) is the electricity price. The risk factor driving cash outflows (expenses) is the gas price. At current prices, the yearly gas bill is EUR 50m (assume payment upfront) for producing a volume of electric power that can be sold for EUR 55m on the market (assume payment upfront).The electricity and gas price follow a multiplicative binomial distribution with the parameters u=1.8 and d =0.6 (electricity) and u=1.5 and d=0.8 (gas). Also for simplicity, we assume perfect correlation. The objective probability q for an upward movement is 0.5. The risk-free rate is equal 8.00% per yearWhat is the value of the GTPS closest to, if it lives for two years and one binomial step is equal one year? Conduct the valuation on a risk-neutral basis.
More Practical Tools for International Students
Making Your Study Simpler
To make preparation and study season easier for more international students, we've decided to open up Gold Membership for a limited-time free trial until December 31, 2025!