Questions
01:146:447:01 CLINICAL NEUROBIO CN F25 Exam 3
Single choice
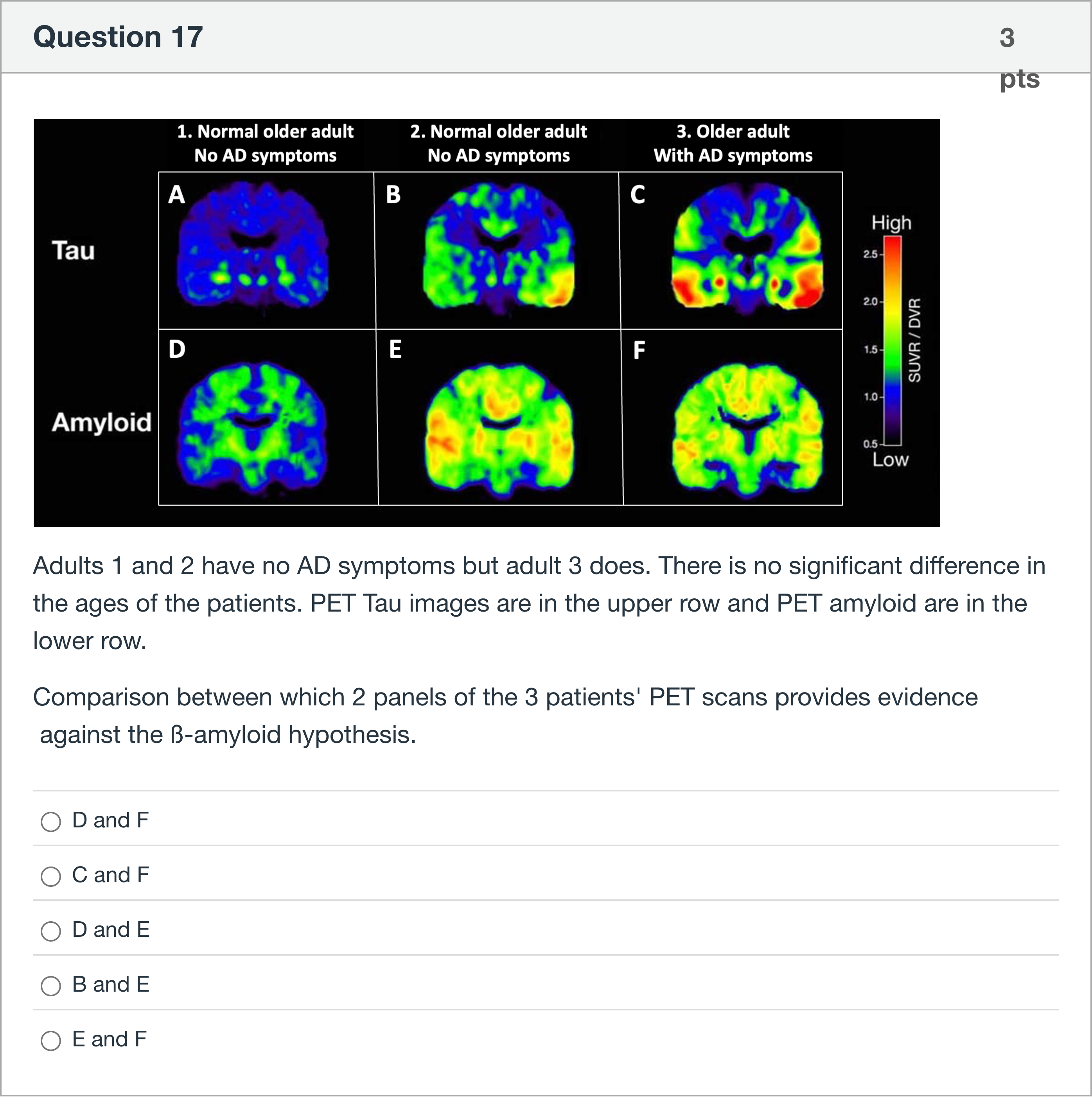
Adults 1 and 2 have no AD symptoms but adult 3 does. There is no significant difference in the ages of the patients. PET Tau images are in the upper row and PET amyloid are in the lower row. Comparison between which 2 panels of the 3 patients' PET scans provides evidence against the ß-amyloid hypothesis.
Options
A.D and F
B.C and F
C.D and E
D.B and E
E.E and F
View Explanation
Verified Answer
Please login to view
Step-by-Step Analysis
To tackle this question, I’ll evaluate what each pair of panels would imply about the relationship between tau, amyloid deposition, and AD symptoms, and how that bears on the beta-amyloid hypothesis.
Option: D and F
- Panel D shows amyloid PET signal in a patient with no AD symptoms (1) and relatively high signal in the amyloid axis. Panel F shows a tau PET signal pattern in the same or a different context. If D and F were the correct pair, one would need to infer that amyloid positivity (D) coincides with tau changes (F) or with symptoms in a way that supports a direct causal chain from amyloid to tau to symptoms. However, in the scenario, adults 1 and 2 have no AD symptoms despite amyloid signals, and adult 3 has symptoms with differing tau/amyloid patterns. This weakens a stra......Login to view full explanationLog in for full answers
We've collected over 50,000 authentic exam questions and detailed explanations from around the globe. Log in now and get instant access to the answers!
Similar Questions
Question at position 65 Which is a correct match of term to definition?Sporadic Alzheimer's disease - occurs when beta-amyloid is affected more than tauEarly onset Alzheimer's disease - occurs when tau is affected more than beta-amyloidSporadic Alzheimer's disease - occurs in people over 65 years oldEarly onset Alzheimer's disease - occurs in people over 65 years old
The diagnostic term for a disease characterized by early senility, confusion, loss of recognition of persons or familiar surroundings, and restlessness is:
The diagnostic term for a disease characterized by early senility, confusion, loss of recognition of persons or familiar surroundings, and restlessness is:
Mrs. A. is becoming forgetful and withdrawing from social interactions with her family. She loses track of time and commonly forgets to eat her meals. The physician diagnoses her with this neurological disorder.
More Practical Tools for Students Powered by AI Study Helper
Making Your Study Simpler
Join us and instantly unlock extensive past papers & exclusive solutions to get a head start on your studies!